|
|
|
14:09 |
|
|
show
|
4:27 |
Hello and welcome to the course Write Pythonic Code Like a Seasoned Developer.
My name is Michael Kennedy and we are going to be on this journey together to help you write more readable, more efficient and more natural Python code.
So what is Pythonic code anyway?
When developers are new to Python, they often hear this phrase Pythonic and they ask what exactly does that mean?
In any language, there is a way of doing things naturally and a way that kind of fight the conventions of the language.
When you work naturally with the language features and the runtime features, this is called idiomatic code, and in Python when you write idiomatic Python we call this Pythonic code.
One of the challenges in Python is it's super easy to get started and kind of learn the basics and start writing programs before you really master the language.
And what that often means is people come in from other languages like C++ or Java or something like that, they will take algorithms or code that they have and bring it over to Python and they will just tweak the syntax until it executes in Python, but this often uses the language features of - let's just focus on Java.
In Python there is often a more concise, more natural way of doing things, and when you look at code that came over from Java, we'll just take a really simple example- if you have a class and the class has a get value and set value, because in Java that is typically the way you do encapsulation, and people bring those classes in this code over and migrate it to Python, they might still have this weird getter/setter type of code.
And that would look completely bizzare in Python because we have properties for example.
So we are going to look at this idea of Pythonic code, now, it's pretty easy to understand but it turns out to be fairly hard to make concrete, you'll see a lot of blog posts and things of people trying to put structure or examples behind this concept of Pythonic code.
We are going to go through over 50 examples of things I consider Pythonic and by the end you'll have many examples, patterns and so on to help you have a solid grip on what Pythonic code is.
So what is Pythonic code and why does it matter?
Well, when you write Pythonic code, you are leveraging the experience of 25 years of many thousands, maybe millions of developers, these guys and girls have worked in this language day in and day out for the last 25 years and they really perfected the way of working with classes, functions, loops, and so on, and when you are new especially, it's very helpful to just study what those folks have done and mimic that.
When you write Pythonic code, you are writing code that is specifically tuned to the CPython runtime.
The CPython interpreter and the Python language have evolved together, they have grown up together, so the idioms of the Python language are of course matched or paired well with the underlying runtime, so writing Pythonic code is an easy way to write code that the interpreter expects to run.
When you write Pythonic code, you are writing code that is easily read and understood by Python developers.
A Python developer can look at standard idiomatic Python and just glance at sections and go, "oh, I see what they are doing here, I see what they are doing there, bam, bam, bam" and quickly understand it.
If instead it's some algorithm that is taken from another language with other idioms, the experienced developer has to read through and try to understand what is happening at a much lower level, and so your code is more readable to experienced developers and even if you are new will become probably more readable to you if you write Pythonic code.
One of the super powers of Python is that it is a very readable and simple language without giving up the expressiveness of the language.
People coming from other languages that are less simple, less clean and easy to work with will bring those programming practices or those idioms over and they will write code that is not as simple as it could be in Python even though maybe it was a simple as it could be in C.
So when you write Pythonic code, you are often writing code that is simpler and cleaner than otherwise would be the case.
If you are working on an open source project, it will be easier for other contributors to join in because like I said, it's easier for them to read and understand the code at a glance, and they will more naturally know what you would expect them to write.
If you are working on a software team, it's easier to onboard new Python developers into your team if you are writing idiomatic code, because if they already know Python it's much easier for them to grok your large project.
|
|
|
show
|
3:56 |
What areas are we going to cover in this class?
Well, we are going to start with the foundations and this concept called PEP 8.
So, PEP 8 is a standardized document that talks about the way code should be formatted, and even some of the Pythonic ideas and Pythonic code examples.
However, we are going to go way beyond PEP 8 in this course, and so we'll probably spend 15 minutes talking about PEP 8 and then we'll move onto other foundational items.
Then we are going to focus on dictionaries, dictionaries play a super important role in Python, they are basically the backing store for classes, they are used for data exchange all over the place, and there are a lot of interesting use cases and ways in which dictionaries are used in a language.
We are going to talk about a lot of interesting aspects and optimal ways to use and leverage dictionaries.
Next up are working with collections, things called list comprehensions and generator expressions.
And we'll see that Python has a lot of interesting flexibility around working with sequences, and we'll see the best way to do this here.
Next, functions and methods.
This will include the use of things like lambda expressions for small inline methods, as well as returning multiple values from methods and that sort of things.
There is a lot to look at to write Pythonic functions.
One of the great powers of Python is the ability to import or pip install a whole variety of packages, there is even a great xkcd cartoon about importing packages in Python, and we'll see that there are a lot of interesting Pythonic conventions around working with packages and modules.
Next up, we are going to look at classes and objects.
Object oriented programming in Python is a key cornerstone concept, even though it may play a slightly less important role than languages like Java and C#, still, classes are really important and there is a lot of idiomatic conventions around working with classes, we'll focus on that in this section.
Python has a lot of powerful ways of working with loops, one of the first giveaways if somebody is brand new to Python is they are not using loops correctly, so we'll talk about when and how you should use loops and we'll even talk about the controversial else clause for "for...in" and "while" loops.
Next, we'll talk about tuples.
Tuples are smallish, read-only collections that let you package up related possibly heterogeneous data and pass it around, If we go into a basic database queries and the built in DB API you'll see that the rows come back as tuples.
Some of the powerful techniques we'll learn about loops involve tuples and we'll see that tuples in general play a really important role, and there is some powerful and useful conventions around working with tuples in Python.
Finally, we are going to look beyond the standard library, with something I am calling Python for Humans; one of the great powers of Python is the ability to go out to PyPi and grab one of the over 80 000 packages, install them using pip or something like this and add amazing powers to your application.
People who are new to Python often skip this step and they look at something they have to do and are just like OK I think "I can implement it in these 20 lines of code".
It's very likely that there is already a package out there that you can use to do this, so we are going to study two packages one for HTTP and one for database access to really bring home this point of look to PyPi and look to open source first before you start writing your own algorithms.
Of course, over time, we may add more topics than what are described here, I am sure as more and more people take this class they will say, "Hey Michael, did you think about having this", or "I also consider this little bit to be idiomatic." Now I don't want to just grab every single detail that I can find, that is possibly Pythonic code and cram it in here, I want to cover the stuff that's most important and not waste your time, but of course, I am sure we'll hear about some new ones that are great and those may be folded in over time.
|
|
|
show
|
0:19 |
We are going to write a lot of code in this course.
And you want to download it and play with it and experiment with it and so on so of course I am going to put this into a GitHub repository, here you can see github.com/mikeckennedy/write-Pythonic-code-demos so I recommend that you go out there and star this so you have it as a reference.
|
|
|
show
|
0:18 |
Are you brand new to Python?
Well this course assumes that you have some basic knowledge on how to create functions, classes, loops, those types of things, and we focus really on the best way to do those.
So if you are brand new to Python, I recommend you check out my course Python Jumpstart By Building Ten Applications and you can find that at talkpython.fm/course
|
|
|
show
|
1:59 |
Before we get to the actual code examples, let's really quickly talk about setup, tools, versions, that sort of thing.
So, this course is built with Python 3 in mind.
If you don't have Python 3 installed, you can get it for your operating system at Python.org/downloads, or you can "Homebrew" or "apt get install" it.
That said, most of the topics will actually be quite similar between Python 2 and Python 3, so we'll talk about Python 2 whenever there are significant differences.
You may be wondering why are we talking about Python 3, when Python 2 is more widely used today in commercial applications.
Let's look at Python over time and I think you'll see why I made this decision; if we start at the beginning, back in 1989, Guido started work on Python.
1991, Python 1 came out, 2000 Python 2, and then, in 2008 Python 3 came out, and this was the first major breaking change to try to improve and clean up the language from all the years that had preceded it.
Well, there was limited adoption because people already had large working code basis, a lot of the PyPi packages were not updated and so on, now if we look at today Python 3 has default as much more common than it has been but more importantly, if you look just four years into the future, not far at all, you will see that Python 2 is "end of life", there will be no more support for Python 2 in less than four years.
And that means, whoever has projects, written in Python 2 have to not just start upgrading them, but complete the upgrades by then.
So I expect there to be quite a pick up for Python 3 and I think focusing on Python 3 is very important going forward.
Guido Van Rossum and the core developers feel this way as well, if you look at the last three keynotes, there has been something like this where Guido has gotten up at PyCon and said, "There is not going to be another version of Python 2, going forward it's all about Python 3." So, that's why this course itself is based on Python 3, even though like I said, differences are quite minor for the topics we are covering.
|
|
|
show
|
1:05 |
So you can use any editor you would like, however, I am going to use PyCharm.
One, because I think PyCharm is the best editor for Python, two- because PyCharm actually detects and warns you and sometimes even automatically corrects errors when you write code that is not Pythonic.
This has to do with naming, this has to do with structure, all sorts of cool things.
So I am going to be using PyCharm in the videos and I encourage you to get it as well.
You can get it at jetbrains.com/pycharm.
If we open that in our browser you can see here is the PyCharm page and if we go to download it, you'll see there are actually two versions, there is the PyCharm community edition which is 100% free, and there is the PyCharm professional edition and if you look at the place where the features are missing from the community edition, it's really around things like database, web and profiler information as well as some of their Docker support.
So, for this course you should be able to use the community edition, I love this tool, I pay for it so I am going to be using the professional edition.
It works great on OS X, on Windows and on Linux.
So whatever operating system you use, you should be able to use it.
|
|
|
show
|
2:05 |
Welcome to your course i want to take just a quick moment to take you on a tour, the video player in all of its features so that you get the most out of this entire course and all the courses you take with us so you'll start your course page of course, and you can see that it graze out and collapses the work they've already done so let's, go to the next video here opens up this separate player and you could see it a standard video player stuff you can pause for play you can actually skip back a few seconds or skip forward a few more you can jump to the next or previous lecture things like that shows you which chapter in which lecture topic you're learning right now and as other cool stuff like take me to the course page, show me the full transcript dialogue for this lecture take me to get home repo where the source code for this course lives and even do full text search and when we have transcripts that's searching every spoken word in the entire video not just titles and description that things like that also some social media stuff up there as well.
For those of you who have a hard time hearing or don't speak english is your first language we have subtitles from the transcripts, so if you turn on subtitles right here, you'll be able to follow along as this words are spoken on the screen.
I know that could be a big help to some of you just cause this is a web app doesn't mean you can't use your keyboard.
You want a pause and play?
Use your space bar to top of that, you want to skip ahead or backwards left arrow, right?
Our next lecture shift left shift, right went to toggle subtitles just hit s and if you wonder what all the hockey star and click this little thing right here, it'll bring up a dialogue with all the hockey options.
Finally, you may be watching this on a tablet or even a phone, hopefully a big phone, but you might be watching this in some sort of touch screen device.
If that's true, you're probably holding with your thumb, so you click right here.
Seek back ten seconds right there to seek ahead thirty and, of course, click in the middle to toggle play or pause now on ios because the way i was works, they don't let you auto start playing videos, so you may have to click right in the middle here.
Start each lecture on iowa's that's a player now go enjoy that core.
|
|
|
|
13:52 |
|
|
show
|
1:54 |
Are you ready to start looking at some Pythonic examples and writing some code?
I sure am, we are going to start by focusing on PEP 8.
And some of the very basic structured ways in which you are supposed to write Python code, and then we'll quickly move beyond that to more the patterns and techniques that we are going to talk about for the rest of class.
So one of the first questions about this idiomatic Python code, this Pythonic code, is "Who decides what counts as Pythonic and what doesn't?" The way one person writes code may very well be different than the way another person likes to write code, and this is one of the reasons that exactly, specifically stating what is Pythonic code and what does it look like is a challenge, but there is a couple of areas where we might take inspiration and pull together some sources and find some consensus.
One of them is just the community.
We can look at blogs, Stack Overflow, things like that and see what people are saying and what they agree or disagree upon.
So, here is a question that asked what is Pythonic code and there is some examples given.
Another area that people take inspiration from is something called The Zen of Python, and if you want to look at The Zen of Python, this is by Tim Peters you can just type import this inside of the REPL in any version of Python and you'll get this, and it's things like "beautiful is better than ugly, flat is better than nested, errors should never pass silently"; again, this is not super concrete but it does give some sort of structure about what is important and what isn't.
We also have PEP 8, Python Enhancement Proposal 8, one of the very first official updates to the Python language was this thing called PEP 8 which is a style guide for Python.
Mostly this talks about the actual structure of your code, like "you should use spaces, not tabs", those types of things, but it also has some guidance on patterns as well.
We'll look at the few of the recommendations from PEP 8 before we move on to the more design/pattern/style recommendations.
|
|
|
show
|
3:59 |
The first PEP 8 recommendation that we are going to look at is around importing modules and packages.
So let's switch over here to PyCharm and have a look at some not-so-great code.
You can see on line seven here, we are importing collections, the recommendation from PEP 8 is that all module level imports should go at the top, unless there is some sort of function level import you are doing kind of unusual, conditional things.
And notice there is a little squiggle under here, and that's actually PyCharm saying "here is a PEP 8 violation, a module level import is not at the top of the file." So we can take this and put it at the top of the file, now everything is happy.
So let's look at few other things we can do, we could say "from os import change directory, change flags and change owner." This is a good way to import a bunch of items from os and not have to state their name, we could do this a different way, using what's called a wildcard import, we could say from os import *, now that would import the three listed above, but it would also import every symbol defined in os.
Now what's wrong with this?
Imagine up here I imported another module, from my module import path, so if I write this code, line four and line six, path is not going to be what you think it is, because we are importing path here but then we are importing every symbol from os using what is called the wildcard import, and os also has a path so it is going to overwrite the definition of path here.
So it's why it's always recommended to use this style of importing.
You may wonder why this is gray in PyCharm, PyCharm is just trying to help us out saying "here are some unused imports you can actually remove", but if I write something like "c = chdir", then that part will go away.
But of course, because we are importing the same thing twice basically it's also saying, I'll move that.
Here we go, so now it says "you are using change dir, change owner but not change flags", down below it's using "change owner".
All right, now "change flags", if I do something with that, it also lights up.
All right, so there was never a problem with that import, that was just PyCharm trying to tell us "hey, look out, you are actually not using that import." Another mistake that people make is they might say something like this, "import collections, os" and let's say "multiprocessing", they may put multiple imports on a single line.
That also works just fine, however, again, PEP 8 recommends that you put one import per line so it's very clear line by line what you depend on here, so we could fix this by saying, let me just put a "no:", something like that, and we could of course fix this, like so, "import os", "import multiprocessing".
So this would be the recommended way to write what was on line four.
So let's look at that import guidance a little more clearly.
Here we have at the top two bad styles of imports, first line: "import sys, os, multiprocessing", on a single line; PEP 8 says "do not import multiple modules on a single line", and avoid "from module import star", these wildcard imports because you may accidentally, unknowingly overwrite other imports.
So we have our better set of imports, "import sys, import os, import multiprocessing", and these of course are going to allow us to use "module name.symbol" name so "os.path" for example, in this sort of namespace style, and that's really nice to know where the particular symbol that you are working with, like "path", where it came from.
If you don't want to use that namespace style, you can use the final import we have here, "from os import path, change mod and change owner".
PEP 8 also have some guidance on the order and grouping of your imports.
It says the standard library imports should go at the top, related third party imports should go in a little section below that and then finally, local app other models within your own code should be put last.
Of course, all three of those go at the top of the file.
Another thing that's nice about PyCharm - it does this for you automatically if you hit Command+Alt+L for reformat file.
|
|
|
show
|
2:47 |
Next up, code layout.
Let's see what PEP 8 has to say about it.
The most important part about code layout that PEP 8 talks about is indentation.
So, imagine we have a method called some_method(), it says that you should indent four spaces, and PyCharm of course, as you've seen, knows PEP 8 and indents four spaces for us automatically, so: one, two, three, four, there we are.
And, we can write something so we could define a variable, hit Enter, like an "if" statement, so something like "if x is greater than two", enter; Python does not like us to use tabs, PEP 8 recommends we use spaces and every indent is four spaces, but it even looks like if I hit tab and delete tab and delete, hit tab, back and forth, it's actually four spaces and PyCharm just treats blocks of four spaces like tabs for us so that it's easier for us to work with.
Next, PEP 8 also talks about spaces between methods and other statements, so for example here it says there should be two blank lines between this method and anything else, somewhere down here two blank lines, two blank lines, I can go and fix this, but if I hit Command+Alt+L it will actually fix all of those spaces for us.
If we look within a method, PEP 8 says there should be either zero or one blank line between any section of that method, and use the blank line sparingly but to indicate a logical grouping; so you can see maybe we wanted to define x and later have this if statement, that would be fine, but if we go farther you can see "hey, PEP 8 warning, too many blank lines", put that back.
Last thing that I'll highlight is around classes, so if we have a class called AClass here, you can see it has three methods, and just like functions, it should have two blank lines separated in it from other module or level things like the top of the file, the method down here, and so on, but within the class, there should be one blank line between methods, not two.
So that's different than functions, when you are looking at methods within a class, it's a little more tightly grouped as you see here.
So let's look at that in a diagram, here we have our method, you can see the little dashes indicate spaces, which have all of our symbols within our method indented four spaces, additionally four more spaces for loops and conditionals and more and more as you nest those things, right, there should be two blank lines between methods, classes and other symbols defined within your module, and finally, PEP 8 recommends that you don't have lines longer than 79 characters, although there is a lot of debate around the value of exactly 79, but you know, it's a guidance, basically try to avoid having super long lines but don't do so by changing your code structures so much that it becomes small, so for example don't, like, create all your variables to just be one character so that when you combine them in some expression they still fit on the line, you would be better off using the continuation, but the idea of not having really long lines of code that's a good idea.
|
|
|
show
|
2:08 |
Next, let's look at what PEP 8 says about documentation and docstrings.
Here we have our some_method, method that I wrote, and I added three more parameters, if I come down here and I say some_method, see there is sort of note help in the IntelliSense, and if I say "look it up", PyCharm does a little work to say what the type hints would be if it could look at the types the way the function is written, but it doesn't tell me really what a1, a2 or a3 mean, or what the method itself does, and obviously it's poorly named, so this doesn't help as well.
So what we should do is give it some docstrings, and docstrings are just a string by itself on the first line of the method, or module, if you're documenting the module or class, if you're documenting the class.
So we can just say triple quote and then I hit Enter and PyCharm will actually look at the method and help us out, so it knows it returns a value and it knows it has three parameters called a1, a2 and a3, so when I hit Enter, I get the sort of structured way of documenting my method so we'll say something like "some_method returns a larger of one or two", which is not actually what it even returns, it's just a silly method I threw in there to talk about spaces, let's say this is a meaningful thing, and let's say this will be the first value will be first item to compare I will say a2 is the second item to compare and a3 is actually whether or not it should be reversed which again, doesn't mean anything.
We'll say 1 or 2.
So if we write this we can come down here now and I say some_method, and look at it I could hit F1 or if I was in REPL I can type "help some_method" and I would see this- some method returns the larger of 1 or 2, a1, first item to compare, a2 second item to compare, a3 should reverse, 1 or 2.
All right, so that's helpful, this is the recommended way to write these docstrings, according to PEP 8, let me fix this, put a little space here, we'll go back and look at the picture.
So the recommendation from PEP 8 is we should write docstrings for all public symbols, modules, functions, classes and methods, and they are not really necessary for non-public items, that's an implementation detail and you can do whatever you want there.
|
|
|
show
|
3:04 |
Let's talk about naming conventions.
PEP 8 actually says a lot about how you should name your functions, methods, classes, and other symbols in your code.
Before we get to the specifics, I just want to give you one of my core programming guidelines around naming, and that is: Names should be descriptive.
Let's imagine you are writing a function.
If you write the function and then you start to put a comment at the top to describe what that function does, I encourage you to stop and think about just making the concise statement about what that comment is the name of the function.
I am a big fan of Martin Fowler's reafctoring ideas and especially the "code smells" that he talks about, and "code smells" are things in code that are not really broken but they kind of smell off, like a function that is 200 lines long, it's not broken, it just doesn't seem right.
It sort of smells wrong, right, so breaking that to a smaller bunch of functions through refactoring might be the solution.
And when he talks about comments he says comments are deodorant for code smell, instead of actually fixing the code so it's remarkably descriptive and easy to understand, people often put comments to say "here is this really hard to understand thing, and here is the comment that says why it's this way or what it actually does or maybe in my mind, what it really should be named." So my rule of thumb is if you need a comment to describe what a function does, you probably need a better name.
That said, let's talk about how PEP 8 works.
So here is some code that is PEP 8 compliant.
We have a module called data_access and modules should all have short, all lower case names and if needed for readability you can put underscore separating them.
Next you see we have a content that does not change during the execution of our code, it's called TRANSACTION_MODE and I forced it to be serializable.
These should be all upper case.
Classes, classes have cap word names, like this, CustomerRepository, capital C capital R.
Variables and function arguments are always lower case, possibly separated with underscores as well; functions and methods lower case, again, possibly separated with underscores.
And if you happen to create your own exception type, here we might want to raise a RepositoryError and it derives from the exception class, when you have exceptions they should always be named in error, so "SomethingError".
Here we have RepositoryError.
As you have seen in other cases, PyCharm will help us here, notice I renamed other_method, here to be Javascripty style with the capital M and not the underscore, you hover over it PyCharm will say "no, no, no, you are naming your functions wrong." It'll even let us hit Alt+Enter and give us some options about fixing this up, it doesn't quite understand how to rename it for us but at least it gives us the option to go over here and do a rename.
Now this is not this renaming in place, but this is a refactor rename across the entire project, so if we had hundreds of files, docstrings, that sort of stuff, this would fix all of those.
It'll show us where it's going to change, here we don't have anything going on really so it's just this one line.
Now, our warning is gone.
|
|
|
|
32:10 |
|
|
show
|
5:57 |
Now that we've got more or less obvious PEP 8 items out of the way, let's talk about a handful of what I consider foundational items.
They don't fit neatly into some classification like loops, or classes or something like that, but they are really important so I put them at the beginning.
The first thing I want to talk about is what I am calling truthiness, the ability to take some kind of symbol or object in Python and test it and have it tell us whether or not it should evaluate to be True or False.
So just to remind you in case you don't remember all the nuances of truthiness in Python, there is a list of things that are defined to be False, and then if it's not in this list, if it doesn't match one of the items on the list, it's considered to be True.
So obviously, the keyword "False" is False, empty sequences or collections, lists, dictionaries, sets, strings, those types of things, those are all considered to be False even though they are objects which are pointing to real live instances.
The numerical values zero integer and zero float are False, "None", that is the thing that represents pointing to nothing, is False and unlike other languages like say C where the null is actually defined to just be a sort of type def back to the zero, "None" is not zero but it's still considered to be False.
And if you have a custom type you can actually define its truthiness by in Python 3 defining a dunder bool, or Python 2 dunder non-zero.
All right, if you are not on that list, then whatever you are testing against is True.
Now let's just review, that's not Pythonic code per se, so let's see how this leads us to Pythonic behavior around testing for True and False.
All right, here I have a real basic method I call print truthiness, and let's just test it here, I can say print the truthiness of True and we could also test False I suppose, so if I run this, no surprise, True is True, False is False and you can see we are using this ternary statement here, "TRUE if" expression, "else FALSE".
Now we are not saying if expression == True, we are using the implicit truthiness of whatever it is that we are passing, here it's the True and False values, but it could also be a sequence, it could be some other kind of expression, all right.
So the recommendation for Pythonic tests on True/False like this is to do something along these lines, it's to actually use the truthiness inherent in the object itself, so you would say something like if I had a val, let's just say it's 7, I would say "if val" and down here I would do something, I wouldn't say "if value == True", or "if value is not equal to zero", I would just use the implicit truthiness that here is a number, if it's non-zero, which in theory I was testing for, it's True, otherwise it's False.
So let's see this for sequences, so if I have some sequence, let's make a list, it could be a dictionary or whatever, we could print the truthiness of empty list and we could have our sequence here, and you can see an empty list is False, but now if I add something and I run it again, and I test for the list with one item, then you can see, now it's coming out to be True.
You can see we can put in here numbers like zero, we can put in 11, or even -11, and zero of course is False, the others are True.
Now we can call this function print_truthiness on "None" as well, maybe leave a little comment here, we'll say "for none", if we pass None, it's going to evaluate to be False, this is not the best way if you are explicitly expecting None to test for it we'll talk about that as a separate item, finally we can define a class called a class or whatever you want to call it and maybe it's going to have some kind of internal collection, we'd like to surface that so we could use the instance of this class itself in a sort of truthiness way, so down here we'll give it some data like a list here, we'll give it the ability to add an item to its set and then we'll go over here and since it's Python 3, we are going to define dunder bool and here for bool we can define one of these ternary statements, we can say "return True if self.data" and just leverage the truthiness of data itself, "else return False".
And then once we do this, we can come down here and say "a = AClass()", we can print and of course if we run it empty, we would expect it to be False, and there it is, it's False, now if we add and item to it and we print it again, now it evaluates to True.
So the Pythonic expectation here or the Pythonic style is when you are testing objects, leverage their implicit truthiness, now we'll write something like "this is True if the length of data is greater than zero." Now, we don't want to write that, we just want to say "if data", it has an implicit truthiness and we are going to leverage that.
So here you can see we've got basically the same code, True if the expression evaluates to True, via its implicit truthiness, else we'll state False, we've got empty collection and it evaluates to False.
We add something to the collection and it evaluates to True, however notice we can't actually test the data equal to True so we can't say print me the truthiness of "data == True" because that's False, these are not the same things, you are basically comparing a list to a singleton True value, a boolean which never is going to be equal, so it's always going to say False, but we can leverage the truthiness of data and it will come back as True.
Finally, if we are going to create a custom type that is itself imbued with truthiness, we give it a dunder bool method and then we just return True or False, depending on how we want it to behave.
You can see below our empty version is False, our non-empty version is True.
|
|
|
show
|
2:23 |
Next let's look at testing for a special case.
Imagine that we are going to call a function and that might return a list and that list might have items in it or it might not, maybe we are trying to do some kind of search and there is just no results, and yet, if it was an unable to perform a search, we'd like to indicate that differently than if there is just no results.
In that case, we can actually change our algorithm just a little bit and test for something different.
Let's look at PyCharm.
So here I have this function called find_accounts and you give it some search text; it checks to see if the database was available and if it's not available, it returns None, which we know is False.
Otherwise, it's going to actually do a search against our database and return a list of account ids.
However, there might not be any matching results in which case that list could be empty, so you might be tempted to say "if not accounts", then maybe I want to just like print something out like this, "else", let's actually try to say we are going to print the accounts.
This part is going to work fine if there are results, we would list them.
However, it could be that our search just returns no results, in which case this list would evaluate the False, so we are going to change this, we are going to test actually if accounts is None, when you are testing against singletons, and None is a singleton, there is only one instance of it per process, we'll use "is" and that actually compares at the pointers, not just the inherit truthiness of the objects or some kind of overloaded comparison operator.
So now our code is going to work as expected, if we literally get nothing back because the DB is unavailable, then we can say oh, DB is not available, otherwise, we might print them out.
And of course, that set might be empty, we might want to put in additional testing here to say "well, if it's empty" like your search works but there is no results, whatever.
But the Pythonic thing here is to notice that we are using "is" to test against singleton and a special case of singletons of course is the None keyword, which is one of the most common.
So here we have this in a graphic, so we are calling find_accounts, giving it some search text and we are going to get some results back and we want to make sure that not only is it truthy, but it's actually worth specifically testing that there is something we got back rather than a None pointer, so "if accounts is not None", and notice, when you negate "is", you say "is not", rather "than not account is", which would also work but is less Pythonic.
|
|
|
show
|
6:18 |
Now let's talk about multiple tests against a single variable.
What do I mean by that?
Here is an example, suppose we have an enumeration of moves, North, South, East, West, North-East, South-West, things like that, and we would like to test is this a horizontal or vertical move or is it a diagonal move?
So somehow we have received a move called "m", from somewhere maybe this is in a game or something, and we want to check is it one of the direct, vertical or horizontal ones so we would say "if m is North, or if it's South, or if it's West, or if it's East, then we are going to match this case." So this is very common in many languages but in Python, we'll see there is a more Pythonic way of doing things.
So here we are in PyCharm and we have basically the situation I just described.
You can see we are in our moves enumeration and it has these various moves, the four horizontal-vertical ones and the four diagonal ones, and it even has a parse method here, parse static method and we are going through and we are actually checking hey if we are given a text and the text lower case version is "w" then we are going to parse that to West, if it's "e" then it's East, "nw" is North-West and so on.
Now we'll see if we can actually improve on this as well but that's not the point of this conversation, OK, so we are going to run our code and it's going to ask for which direction we want to move, North, South, East, West and so on and we'll use that parse method you just saw.
If it's something it doesn't understand it returns None and as we already discussed we check if it is None, then we bail or print it out so just you can see what the parse did as and and then here is this code that we have before.
So, let's first run this to make sure it works, OK, "which direction you want to move?" Let's go South-West, move South-West was parsed, hey that's a diagonal move; we'll try another one, let's try North.
North, that's a direct move, maybe the name is a little off but you get the idea.
So let's write in more Pythonic version here.
recall in Python that if we have a collection, like a set or something like that, if we say "s = {1,2,9,11}", we can check for containment and in this set using the "n" keyword, so if we have "v = 11", we could ask we could say "print v in s" and because 11 is in the set it should come back and say yes, so let's just say something here, True, yes it's in there.
We change this to 12 and run it again, we'll see it False, it's not in there.
So we are going to use this principle to make our test more Pythonic.
So we can make this shorter, less error-prone, easier to read and more Pythonic using that idea, so what we'll say is "if m is in the set of moves to the North, moves to the South, moves to the West or moves to the East", like so, we could use a list, we could use a dictionary, but set seems like the right things for what we are trying to express here.
Let's just run it and make sure that this still works.
So if we move North, it's a direct move, if we move South-East that's a diagonal move.
Let's just try, let's take West, boom, direct move.
OK, so that's pretty sleek, right?
So when we have a single variable and we want to test it against multiple conditions, use this "in" keyword, now this is extremely readable, but in fact, it would be a little bit slower, so most of the time, a little bit slower in something like this is you know, a millisecond here, a millisecond there, nobody cares, it doesn't matter.
But if this happened to be within a really tight loop, we could improve upon this by taking this set we want to test for and moving it outside the loop.
So we could do some kind of refactor and create a variable here and call this say a direct_moves, like that; where this gets put somewhere outside of our loop and then inside of the loop we can test it like this, again this should still work, just like before; North, yes that's a direct move, but sometimes you may want to avoid this for performance reasons.
Let's just do a quick little test to actually understand what the performance implications are.
So here we are going to do a "for...in loop" one million times and let's start out with the version that is not so Pythonic with the multiple tests, we'll just compute the boolean over and over and over and see how long that took.
So let's run this.
So it took 0.2 seconds, so 200 milliseconds for a million moves, chances are this doesn't really matter for you, but if we want to figure out how long that took for one, we could do something like this, so 10 to the -7, extremely fast but like I said, if you do it in a million times, hey maybe it matters, let's test a version that is more Pythonic but slightly slower.
Here 0.3 instead of 0.2, no big deal, however we wanted allocating the set each time to the loop, you'll see this is fairly slower.
So 2 seconds, instead of 0.2 seconds, so that's like 10 times slower, so you really have to decide how much does this performance matter you can see it's almost entirely negligible when you extract it outside of the loop, and you write it like this, it's still quite fast but it does put indent in when you do it this way.
So here I commented out a little test if you want to play with it, feel free to uncomment it, you should really thrive to do this, this sort of test here, and maybe I'll make it the most readable version until we have a performance problem, so we can inline this here, excellent, so here is a nice Pythonic way to test a single variable against multiple values in Python.
So this is probably the most natural way to write this code coming from somewhere like C++, Java, C# and so on, however, in Python we can use this set and the "n" operator to make this much readable, now if we want to see all the cases, it's very easy just look at what's in the set if you want to add or remove one easy to do and you won't miss an "or" with an "end" or drop a parenthesis or something weird like that.
|
|
|
show
|
3:32 |
This tip is nice and short but really helpful.
So let's talk about how we choose a random item.
Here in PyCharm, first I want to show you the bad what I am calling C-style but this appears in many languages.
So we have these letters, and letters and numbers, we'd like to randomly pick one and show it to the user.
So the most natural thing to do coming from a language like C is to create a random number that will be a proper index into that list, so we'd say "index = rand", we create "rand" and "n" be from 0 to the "len" of letters.
And we'll say "item = letters of index".
Now, this actually includes the upper bound so we need to take one away from it to make sure we don't have an off-by-one error, but of course, this is something you have to go look up in the documentation to see - is it including the upper bound and lower bound or just lower bound?
Something like this.
And we can just print out the item, if I run it, apparently "y" is the randomly selected one run it a few more times, "zero", "w", "k", awesome.
So what's wrong with this?
Well, there is a couple of things.
One, I have to go and calculate the length I have to know this is including the upper bound when I ask for these random numbers, so I have to do minus 1, oh and I forgot to check that there is actually an item in here that the index is not negative, something like that.
So let's write the Pythonic version.
You'll see it's easier to read, it's shorter, it's safer, everything you want.
So, I want a random item, and given a sequence, I can just say "random, choose a random item", from that sequence.
Done, I don't have to think about what the documentation says about upper and lower bounds, I don't have to verify anything, just print out the item, run it again, "c" was chosen by the C-style, and "d" by the Python style.
"b", "z", "4", "t", and so on.
Simple, sweet, but very effective and once you start using it, you will never want to go back to the C-style.
So here is that code in a graphic.
We have the bad style using the "random int", oh and you can see in my slide we actually have a bug about the upper bound, how interesting, huh?
There, I fixed it, but it was interesting that we had this place where we could introduce the bug and of course we get the index, we use the index to index into the letters, get the item and then we can print it out.
The Python one instead let's just go random that choice, from a sequence, boom, there you go.
In Python it's generally preferable to use declarative code rather than procedural code, and this is a little step in that direction.
|
|
|
show
|
7:07 |
Let's talk about string formatting and building up strings from fundamental values.
Over here in PyCharm we have two variables, a name and an age, Michael and 43.
We'd like to create the string "Hi, I'm Michael and I am 43 years old", given whatever values those variables have.
If you are coming from some languages like say C# or Javascript, you may try to go do something like this, you might say, "Hi", so if we try to run this, it's actually going to crash, you can see PyCharm is even pointing that out, it says there is something wrong with this age and this string concatenation here, boom, crash, cannot convert integer to string implicitly.
So this version is obviously not Pythonic, right, the deal is Python is not going to implicitly convert that to a string for us so we could say "crash, don't do this".
There is some other ways to do this, we could come down here and say if it's not going to implicitly convert this to a string, we can do that.
Now, this actually works.
We are done!
Not really, we are writing bad Python code, when we write this, so this works, but not Pythonic at all.
So, another way that we can do this is we can use a format string, so I can come down here and say, we are going to put a string and here we are going to put a number and I'll use "d" for integer, and then I can do a % format here and give it a tuple, so name and age, now format that in a little there, now if we run it, you can see exact same text.
So this is probably Pythonic, this is very common, but it's also an older format, it has a lot of limitations, so for example, if I was giving the age but the age was presented to me as actually a string, well, then this crashes.
What's on line 13 is not bad and is used quite widely, it does have some problems.
For example, you have to very carefully know what the type is, so I could do my "%d" with age because that was a number, but if it happens to be that it's just a string that represents a number, or could be converted to a number, well, again, a crash.
So there is a new, more modern style that works in Python 2 and in Python 3, I am going to decree this style to be Pythonic, so if we take the same code and I'm going to come here and say "I would like to just put whatever it's specified first here, whatever is specified second there, and do whatever you need to do to format them", here we go, we can do it like this, so "Hi I'm Michael, I am 43 years old", and it doesn't matter, let's comment this out for a moment it doesn't matter if this is a tuple, it doesn't matter if this is a string, it didn't even matter if it's an object, right, anything you want can go in there and you'll get the best string representation that you are going to get.
OK, so that's nice, really like that, but of course, with this style we do get more flexibility here, I didn't put numbers in here but you can say things like I would actually like the second, this is zero based, the second element to appear first, and the first item to appear second like this, so "Hi I'm 43, my name is Michael", I can even say something like "yeah, {1}" and repeat them, right, so that's excellent.
So I think that this style, which works well in both versions of Python is really the preferred way to do string formatting.
However, we can go farther, suppose I have a dictionary here and it has a day called Saturday and an office called home office, and I'd like to take those pieces of information and say: "On Saturday I was working in my home office." So we could go and do something like this, we could say "print" and let's just say we are going to put some kind of item here, and some kind of item here.
Now I could use the format you see above and just pull the items out of the dictionary but I can actually say "there is a key in the dictionary called day, and a key in a dictionary called office", now I would like to just project this dictionary into that string, and so I can say "format" and then do the keyword unpacking of the dictionary like so, on Saturday, I was working in my home office, so not only do you get more safety around the type you get a lot more flexibility.
You see, you can have additional data in the dictionary but if for some reason one of them is missing, if it's like this, well that's going to crash because it's going to say well, there is no office here, right, so you have to have at least values you are working within a dictionary but they can have more.
Now we can take this once step farther, and I can't show it to you running because I am running Python 3.5, but in Python 3.6 they have taken this idea and said this is a great idea, if we could come down here, let's take this version, so great idea, if I already have like a name, and an age I could come down here and use keyword values, like so and get this to run, right, "Hi, I'm Michael I'm 43", kind of like unpacking our dictionary, but in Python 3.6 they said you know, this is such a common thing, we would like to just grab the variable called name and grab the variable called age and put it in the string, without format.
So if we had just an f right here, then Python itself would actually pull name and age out of whatever namespace it happens to be in.
Now you can see this is an error because it doesn't work, in Python 3.5, but that's coming in the next release of Python, which is awesome.
All right, so let's review.
The first sort of naive version of printing out this string we are just going to concatenate them, that works well with strings but not with non-strings, so our age caused the crash, that was definitely not the way to do it, we could explicitly convert that age to a string, this is definitely not Pythonic, this is absolutely not Pythonic, but it does print put "Hi, I'm Michael I'm 43 years old", we can use the percent format style where we have "%s", "%d", "%f", that kind of thing, but it's restricted only formatting output for integers, floats, under the "%d" and then strings under the "%s".
Anything really that can be converted to a string for those.
But you kind of have to know the format, that's not perfect to my mind.
Some people say they prefer the percent version because there is fewer characters to type, and that somewhat depends on your editor I mean you do have to say ".format" instead of percent, in PyCharm you type ".f" and hit Enter, right, so you type about the same number of characters, so here are the more Pythonic versions in my opinion.
The first version, we used .format(name, age) and then we just put blank curly braces open/close curly braces, no numbers to say that the first item here, the second item there and so on, we have of course the extra flexibility to say "we'd like to reorder those and number them in the string", if we have a dictionary so we can actually project it by key into the string or we could even use keyword arguments on our format to accomplish the same thing, which is really nice because here we have a 1 and zero on a complex strings you might have many of these little indices or whatever, into your arguments and those are hard to maintain.
Whereas keyword arguments are really clear what goes into which part of the string.
Finally, in Python 3.6 coming soon, there is going to be what's called string interpolation, where you put an "f" (format) in front of the string that will automatically grab the data straight out of the variables.
|
|
|
show
|
2:49 |
The next Pythonic tip I want to cover is about sending an exit code to indicate whether your application succeeded or failed.
Let's have a look, so here I have a little utility app, meant to run on Windows and its job is to format the main drive C: and of course you don't want to just do that, just because the app was run, the script was run, you'd like a little confirmation, so here we ask the user "are you sure you want to format your main hard drive?" "Yes" or "no", you can see the default is "no" but if for some reason they type in "yes", and they come down here, we are going to simulate a little work, we are not actually going to format anyone's hard drive, and then we'll say "format completed".
So let's run this.
"Are you sure you want to format drive C?" Let's say "no", format canceled, now notice, exit code zero.
Let's come down here and say "yes", I would love to format drive C, so we do a little bit of work, you can't format it immediately, it's hard job here, and then boom, formatted successfully, enjoy the new hard drive space.
Now, we also got code zero, if I was trying to run this as a subprocess, or I was trying to orchestrate this by chaining it together, there is no way for me to know as a user of this script whether or not the user canceled or they actually formatted the hard drive.
We can easily come up here before a return, we don't technically need to return, because this is going to actually stop executing immediately; anyway, I can go over here and I can import "sys", now I was already importing "sys" so that I could use this little flush command that normally I wouldn't have been there, so I'll say "sys.exit" and we are going to exit here with let's say 1, down here, we can do this, we can say "sys.exit(0)" of course, you saw if we don't do anything at all, "exit(0)" is what is going to happen, so maybe I'll leave this one off.
Now, we also know that this is going to throw an exception so this "return" is actually unreachable, PyCharm told us that, OK so let's try again; "are you sure you want to format your main hard drive?" No.
Exit code 1.
Do you want to format your hard drive - oh please do, exit code 0.
Again, canceled, exit code 1, perfect.
So if there is any chance that your script is going to be called by other script or other applications you want to make sure that you indicate some kind of exit code so that they can use that information to determine whether or not they can continue whatever they are doing afterwards, whether or not your script succeeded.
So if we just let our app, our script exit, well it's always code zero, but we can use "sys.exit" and give some kind of code, typically the convention is if it's non-zero there was some kind of either failure or abnormal exit whereas zero is "all systems nominal".
Everything is good.
|
|
|
show
|
4:04 |
For this next Pythonic concept, let's go back to the Zen of Python.
So here I am in the Python REPL, and one of the core concepts is that flat is better than nested.
Now, it turns out this is one of my favorite items here and one of my favorite programming concepts, because a lot of people seem to do it in the reverse.
I call this sawtooth style of programming, we have lots of loops with "ifs" and conditionals and then more loops and so on.
So let's look at this, how we can apply this in Python.
Over in PyChram, we have a program that is meant to simulate downloading a file, and this might not be the best way to do it, obviously it is not the best way, but it really is a simple example to highlight this "flat is better than nested".
So what we want to do is we want to download a file and we are going to do a series of tests to make sure that we are able to download the file or at least we think we'll be successful before we actually try.
First one uses a little support module here, we are going to ask: "Is the download URL set?" if it is, then we are going to check the network status and then we are going to make sure that the DNS is working then finally we are going to check that we have permission to access the file and if all those things are true, then we are going to try to download it.
Otherwise, we are going to say well, this one goes back here so it looks like no access this one here, no DNS, this one here PyCharm even has little like tiny lines that are probably hard to see but I can follow back up, no network and then finally this one is bad URL.
This is a serious bad piece of mine, I hate code that looks like this, so let's write a different variation of this which I am going to call download_flat().
So let's just reverse these things, let's look at our conditionals here, instead of having these sort of positive checks, yes you can do this and you can do this and you can do this, we can return these "if" statements into what are called guarding clauses, you don't let the method run if one of them is failed.
So I can come over here and say "if not check url", then we'll say oh that's a bad URL.
And we can unindent, that's good, of course now that we are up here we want to return early, we'll say "if not check the network" then we want to say "no network".
And return, and again, unindent, it's better, again, "if not check DNS", do something and then return we'll print out that there is no DNS and then we'll unindent and finally we'll do this "if not this, return", and then if all the guarding clauses pass then write at the very edge of our method, not indented at all as far as this method is concerned, we can write our meaningful code and this makes it so much easier to maintain and write, instead of trying to do our actual work way down inside here.
So this is a very nice way that you can write these guarding clauses instead of this what I call sawtooth programming, so that you have nice, flat, easy to understand, easy to modify things, like for example down here, if I want to insert another test, I've got to make sure I've paired up correctly with the "else" down here and so on, but most importantly, you don't have to work in a hyper-indented way; this also works in loops, you wouldn't return out of the loop but you would just do a "continue" with the guarding clause instead of a test and then put the actual stuff inside the "if" statement.
"Flat is better than nested", let's see that in a diagram.
All right, here is the code that we wrote that was the sawtooth style with the positive checks, "make sure I can do this, make sure I can do that" and so on, and we rewrote that by inserting or converting those two guarding clauses this flat version is much better, we've converted all the positive checks to guarding clauses and it's much easier to add and remove those guarding clauses, see what the "else" clause is that goes with it because now it's right there and most importantly, at the end, we get to work in a non-indented way.
|
|
|
|
44:01 |
|
|
show
|
1:43 |
Now we are going to focus on a really important set of topics revolving around dictionaries in Python.
So, the first question you might ask is like: "Why should we focus on dictionaries in Pythonic code?" Well, it turns out that dictionaries are everywhere in Python, you'll see that dictionaries are the backing store for many types, so for example when you create a new object from a custom class you've created, every instance has its own backing store which is a dictionary for the fields and whatnot that you add to this class.
Dictionaries are isomorphic with JSON, so you'll see that there is basically a one to one mapping between Python dictionaries and JSON which is the web's most important transport type.
If we want to create a method, that allows us to use keyword arguments, one of the ways we can do that is to have the kwargs, **kwargs parameter and this allows us to not just pass a set of non-keyword arguments but actually arbitrary ones as well, and those come through as a dictionary.
As we'll see, dictionaries add incredible performance boost for certain types of algorithms, and we'll look at that in the section as well.
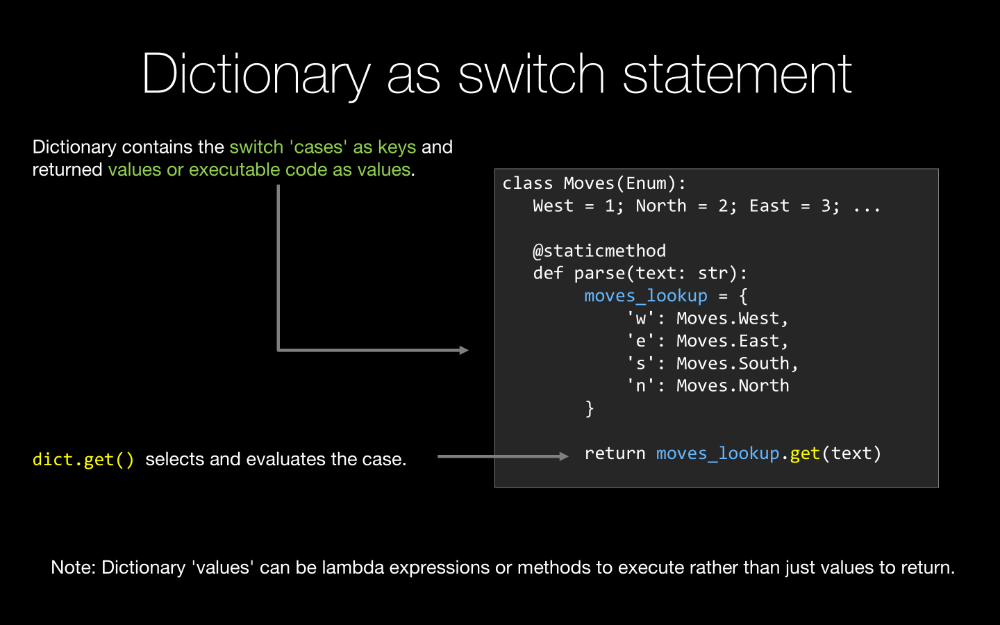
Python, the language does not have a switch statement, and we don't miss it too often but sometimes a switch statement is really nice and you'll see that we can actually leverage dictionaries to add switch statements, switch statement-like functionality to the Python language.
If you access a database and you are not using an ORM such is SQLAlchemy, typically the way the rows come back to you are each row comes back either as a tuple or a dictionary, preferably as a dictionary so you can lookup the columns by name rather than index.
So that's just a taste of why dictionaries are so important in Python, you'll see there is a lot of cool Pythonic techniques around working with them, so let's jump right in.
|
|
|
show
|
9:33 |
The first area I want to cover around dictionaries is using dictionaries for performance.
So when you have a collection of data, the most natural choice, the thing Python developers reach for first, has got to be a list.
It's super common, super useful and very flexible.
Let's look at two different algorithms one using a list and one using a dictionary and we'll compare the relative performance.
So here we have a bit of code and we'll look at this in detail in PyCharm in just a moment, but here is the basic way it works.
So we start out with a list of data, here you can see in our example we are going to be using half of million items, so we are calling a data list and it's going to contain some rich objects with multiple values or measurements - details aren't actually affected.
Then, suppose for some reason we have done some computation and we've come up with a hundred pieces of data we would like to go look up in our list, so we are going to go loop over each of those 100 and then we are going to find the item in the list, we can't just use interesting "item in list" in operator, because we actually have to filter on a particular value, what we did instead is wrote this method called find_point_by_id_in_list and it just walks through the list, it compares the id it's looking for against the ids that it finds in the list, as soon as it finds the match, it returns that one, it's assuming to be unique and then it appends it to this interesting_points.
So this is one version of the algorithm.
The other one is well, maybe we could do a little bit better if we actually used a dictionary.
And then we could index - the key for the dictionary could be the id.
So if we wrote it like this, here we have a dictionary of half a million of items, again the same dynamically discovered 100 interesting points, and instead of doing this lookup by walking through the items, we can actually map the id to the objects that we are looking for so we can just index into the dictionary.
Obviously, indexing into the dictionary is going to be faster, but possibly the computation, the building of the dictionary itself might be way slower, if we are going to do this a 100 times, we have half a million items, right, it's much more complicated to generate a dictionary with half a million items than it is a list.
So let's see this in action and see what the verdict is.
So here we have our data point, our data point is a named tuple, it could have been a custom class but named tuple is sufficient and it has five values: id, an "x y" for two dimensional coordinates, a temperature and a quality on the measurement of the temperature.
You can see I have collapsed some areas of the code because they don't really matter, these little print outs I think they kind of make it hard to read.
In PyCharm you can highlight these and hit Command+.
and turn them into little collapsible regions, so I did that so that you can focus on the algorithm and not the little details.
Here we have our data_list that we are going to work with, and we are going to use a random seed of zeros so we always do exactly the same thing, but randomly, so that we have perfectly repeatable results and then down here for each item of this range of half a million each time through the list we are going to randomly construct one of these data points and put it into our list.
Next, we do a little reordering on the list just to make sure that we don't just randomly access it in order, since we are using auto incrementing ids, next we are going to create our set of interesting ids that we are going to go search through our list, and then later through our dictionary.
Really we would use some kind of algorithm and we would find interesting items we need to go look up, but in this case we are just going to randomly do it, but there is a few Pythonic things going on here, one - notice this statement here with the curly braces, and then one item left to the "for", that means what we are building here is a set using something called a set comprehension and each item in the set is going to be a random number between zero and the length of that list which is half a million, so quite a large range there.
And we are just going to range across zero to 100.
The other thing to look at is we don't actually care about the index coming out of the range, we just want to run this a 100 times.
In Python, when you are looping across something like this range set here or you are possibly unpacking a tuple and there is only a few of the values, not all the values you care about, it's Pythonic to use the underscore for the variable name to say "I must put something here but I actually have no concern what it is." So, our interesting ids are interesting from a Pythonic perspective, but now we have the set of approximately 100 ids, assuming that there is no conflicts or duplication there, and next thing we are going to do is we are going to come along here, we are going to start a little timer, figure at the end what the total seconds pass were, and during that time, we want to go and actually pull out the interesting points that correspond to the interesting ids.
So we are going to go for each interesting id, remember, it's about a 100, we are going to say "find the point in the list like so, and then add it", and if we look quickly at this, you can see we just go through each item on the list and if the item matches the id we are looking for, we are done, otherwise, we didn't find it.
So, just to get a base line, I am going to assume that this is slower, let's go and run it and see what happens.
Remember, it's only the locating data in the list part that is actually timed.
All right, so this took 7.9 seconds and here you can see there is a whole bunch of data points it found, if we run it again, we get 8.4 seconds.
So it's somewhere around 7 to 8 seconds.
All right, so let's take this algorithm here and adapt it for our dictionary.
So I've got a little place holder to sort of drop in the timing and so on, you don't have to watch me type that, so the first thing we want to do is create a dictionary, before we had data_list, now we are going to have data_dict, we can create this using a dictionary comprehension, so that would be a very Pythonic thing to do and we want to map for each item in the dictionary the id to the actual object.
So, we create set and dictionary comprehensions like so but the difference is we have a "key:value" for the dictionaries where we just have the value for sets.
You kind of have to write this in reverse, I am going to name the elements we are going to look at "d", so I am going to say "d.id", maps the "d for d in data_list", right, so this is going to create a dictionary of all half a million items and mapping the id to the actual value.
So now, let's start a little timer, and next we want to locate the items in the dictionary, so again, we'll say interesting_points, let's clear that; "for id", we call it "d.id" so it doesn't conflict with the id built in, so "for d.id in interesting ids" we want to do a lookup, we'll say "the data element is", now we have a dictionary and we can look up things by ids, so that is super easy, we just say it like so, assuming that there is none of the id that is missing, something like that and then we'll just say "interesting_points.append(d)" Oops, almost made a mistake there, let's say "d.id" not the built in, that of course won't work.
All right, so let's run it again and see how it works, so we are going to run, it's still going to run the other slow version, I'll skip that in the video, wow, look at that, 8 seconds, and this is 0.000069 seconds.
So that's less than 1 millisecond, by a wide margin.
That is a non-trivial speed up, let's see how much of a speed up that is, then the other thing to consider as well, maybe the speed up was huge but the cost of computing the dictionary was more than offsetting the gains we had, let's try.
Wow, the speedup that we received was not one time faster, two times faster, or ten times faster, if this is data that we are going to go back into and back into, we would create this dictionary and sort of reuse it, where we get a speed up of a 128 000 times faster and an algorithm that is actually easier to use than writing our silly list lookup and it took literally one line of a dictionary comprehension, that's a beautiful combination of how dictionaries work for performance, bringing together these Pythonic ideas like dictionary comprehensions and so on, it made our algorithm both easier and dramatically faster.
What if we had to create this dictionary just one time to do this work?
Maybe we should move this down and actually count the creation of the dictionary as part of the computational time, so let's see what we get if we run it that way.
Look at that, 8 seconds versus 0.2 seconds, so even though it took a while to create that dictionary it still took almost no time relative to our way more inefficient algorithm using lists, we've got a 37 times speedup if every single time we call this function or we do this operation we would have to recreate the dictionary, it's still dramatically better and of course simpler as well.
Let's review that in a graphic.
So here we have two basically equivalent algorithms, we have a bunch of data we are storing in a list, half a million items, and then we are going to loop over them and we are going to try to pull some items out, by some particular property of the things contained in the list, well if you are in that situation, dictionaries are amazing for it and as you saw they are stunningly fast.
If we don't count the creation of the dictionary, we had a 130 000 times faster the bottom algorithm to the top algorithm.
So I am sure you all thought well dictionary is probably faster, but did you think it would be a 130 000 times faster, that's really cool, right?
It basically means that becomes free to do that lookup, and even if we had to recreate the dictionary every time, it's still 37 times faster, which is an amazing speedup.
|
|
|
show
|
6:15 |
Next, let's talk about taking multiple dictionaries and combining them into one that we can use to look up items that came from various places.
Here in PyCharm, I have a sort of web example for you, imagine that you are writing a web app, there is data coming from different locations into your action method, so on one hand we have routing setup that is passing data through the URL, we might be in that location, passing the id and the current value might be this, the title might be that, we also might have the query string and the query string might have some other value for id, like 1, it might have a separate value it's adding to the mix here called render_fast is True, then maybe we are also, as part of posting long URL which matches the route with the query string we are posting back a form and that form has email, a name and it is well.
So here I am just going to print out these three dictionaries just so you can see what they look like, and no surprise, here they are, they just look like basically they are written here, so what if I want one dictionary that I can just ask - "what is the id, what is the user name or what is the email address?" - and not have to worry about which one is located and we have our super non-Pythonic way here and I am going to use this dictionary called "m1", we'll go like this, and I'll say "for k in" and what we are going to do is we are just going to loop over each dictionary and stick the value in there.
The order in which we do this matters.
So let's suppose we want the query string that has the least value, so we are going to put those values into this combined dictionary first, so we'll say like so, and then we could just go to "m1" and we can just set the value for whatever the key is, to whatever the value and the query dictionary, here's like that.
And, we'll do the same thing for let's say the next thing we are going to do is the post, like that, and finally, we'll do it for the route.
OK, so if we run it, we should get a dictionary because the route has higher priority, with id 27, title Fast apps, render_fast is True and then that data in it.
Let's run it, all right, id 271, like we expected, Jef, Fast apps, perfect, so it looks like you combined it well, but this is a very procedural way, and there is better ways, so in Python down here we can actually sort of improve upon this by leveraging a couple of methods on the dictionary, so we can go like this, and remember we wanted the query first so we can say "query.copy" and actually create a copy of the dictionary and then we can go here and we can say update, I would like you to update your values possibly overwriting them with "post", and then I would also like to overwrite this with the route.
So now if I run it, we should have the exactly the same output but a little safer, less fiddly.
OK, you can see these are the same dictionary, now notice there is nothing about dictionaries that are ordered, so they are going to be out of order but they are the same value, down here this "no", I wrote some code that checks whether these four dictionaries "m1", "m2", "m3" and "m4" are the same.
We are not finished yet, so they are not going to be the same.
But in the end, we write these better versions here, we should be good.
We can actually do this in one line with the dictionary comprehension, it's not pretty but it does work.
So, let's imagine where they end, we can say "for d in" and we can put all of our dictionaries in the order we care about, "query, post" and "route" and so for each one of those we can come back here and say "we would like the key:value" and we'll go for each one of these, we'll say "for k,v in d.items" So here you can see exactly the same dictionary, matching ordering, let's do a little formatting on that.
OK, so we are looping over all the dictionaries and for each dictionary we are looping over, we are looping over and point out the key and the value from the items and then we are creating the dictionary from that.
So, this works, I really don't like it very much, even though it happens in one line and it feels like oh that must be Pythonic because look at it, it's cool and special and declarative.
To me it's hard to look at it and not go "oh, I see you are combining those dictionaries", so given the choice between the classic Pythonic way and this dictionary comprehension way, I would actually prefer the one above, because this is really clear to me what's happening.
Maybe that's just me.
But in Python 3.5 they introduced a really cool way to merge dictionaries, so if we were going call a function, so let's say some function, and we want to take a dictionary and pass it as keyword arguments here I could say **query say, if I wanted to pass the values from the query, but they kind of apply that same syntax here to say I would like to merge all the values from - let's start with query, all the values from post and all the values form route.
so this does not work on Python 3.4 and below so be careful.
It's only Python 3.5 and above, let's run it and make sure it does what we expect.
Boom, look at that, there is a last one we just wrote and if we actually do a comparison of the values ignoring order, these are exactly all the same, so here we have the super non-Pythonic way, we have the sort of classical way of doing this, leveraging the dictionary features, we have the "clever but too clever" in my opinion way of looping over the dictionaries and looping over their key value items and recombining them, and then we have the quite sleek Ptyhon 3 way of the **dictionary to unpack them, back into a dictionary.
And notice, it has the same overwriting process where the id from the query was overwritten by the id from the route because the route came last.
Let's see that in a graphic.
So, here is our three dictionaries and our non-Pythonic way we create a blank dictionary and we just loop over all the items and we just start filling it up, very procedural, not amazing.
But instead, we can use the Python 3 that is 3.5 actually quite high, way of unpacking the dictionary back into a dictionary so this **query **post **route becomes a new dictionary.
Very nice.
|
|
|
show
|
9:03 |
All right, this next tip or technique I want to show you might almost be considered anti-Pythonic.
Let's look at the Zen of Python and see what it says.
So, recall the Zen of Python says "special cases aren't special enough to break the rules", so that leads to a really clean and simple and easy to understand language, often with one way to do things instead of three or four, that's awesome.
However, it also says "practicality beats purity", so let me give you a heavy dose of practicality involving dictionaries, and memory in Python.
So here is the server memory process for the web servers of this company called oyster.com, they do like hotel booking and that kind of stuff.
They wrote a nice blog post about it we'll look at it in a second.
They were storing a lot of stuff in memory, cached, using Python objects, they used this concept of slots which we are going to talk about to go and save 9GB of RAM on their server, and it literally just took one line of code.
This will give us a chance to look inside at the backing store for custom objects, which normally is a really good thing to have, but every now and then can be trouble as you can see here.
So we are over here in Windows 10, and this is oyster.com, you can see it's all about booking hotels that have been checked out by real people, sounds cool.
Here is their blog post talking about how they used slots on this image class that they cache heavily.
Let's go and look at this in a different example that I have created for you in PyCharm.
We are over here in Windows 10 because the tools to look at the process details and understand its memory usage and CPU usage are really great on Windows.
So we are going to work with four types holding the same information, we are going to have a tuple which holds four values, they are unnamed, we are going to have a thing called an ImmutableThingTuple, we are using this name tuple to create it, has values a, b, c and d, we are going to have a regular class, a plain little class that has four values a, b, c and d, storing those on its instance, and we are going to use slots with this what - we are calling an immutable thing, it's a little bit wrong, it's immutable and that it can't have new attributes but the values a, b, c and d, those can change.
By adding the slots here, what we are going to do is, remember, every normal object has a dictionary backing store, and so if I look at "self.__dict__", you would see that it had four entries, a, b, c and d and the values would be whatever the values of a, b, c and d were passed in.
Each instance of mutable thing has its own separate copy of the dictionary, which means it has its own separate copy of the keys as well.
On the other hand, this one when you define slots, it says look, this type holds four and exactly four things with this name and we can put the storage of those slots into the type, which is a singleton, instead of two the instance variables which they are maybe millions.
So, let's look at the code below where we created a bunch of these and we look at the memory pressure and behavior of the different items.
So notice, we have one million items we are going to work with, we want to put them into this list.
What we are going to do, we are going to time every one of these operations the same, we are going to choose one of the four options, loop 1, loop 2, loop 3 or loop 4.
Loop 1 is going to use straight regular tuples and it's going to allocate inline a tuple with four values, n+1, n+2, n+3, n+4 and it's going to put it into our list.
So here we have in memory one million of these tuples, we are going to determine how long that's going to take, here we see "Finished, waiting...
done in" a certain amount of time and this is an input call so it's going to block.
The reason it blocks is I want to process to stay alive so we can go look at its memory graph before it exits.
OK, so you just hit Enter to exit; first, we are going to run this for tuples.
Here you can see it took about half a second, paste it over here so that we can see what the relative performance was, and let's run process explorer, which lets us look down here at the details.
So here is Python, you can see, if we open this up we've got a performance graph, right now it's using a 145.7 MB in private bytes.
So we'll note that here.
Let's run named tuples.
So it's an interesting question to ask, if these absolute bare minimum tuples that can't expand, don't have names, things like that, how do they compare both in performance and memory of our named tuple that we created up here above, like so, using our collections.name tuple.
All right, let's run and see how it works.
OK, well, that is slower, let's go ahead and copy that and put it in our little document here, so it's about three times slower, as you would expect, it's doing quite a bit more work to parse those and so on, let's look at the memory here, the memory is about the same, 143.3 MB, so no big deal.
Let's move down the line here and run it for a standard class, so this one is probably going to have the least good performance from a memory perspective, because remember, every instance could have been modified dynamically at runtime, to have new attributes and so on, so they all have their own dictionary.
Let's give it a shot and find out what happens.
In terms of speed, it's almost identical to named tuples, that's cool, what about memory- wow, memory is little more, like almost a 100 MB more, so 241 MB.
All right, here is where it's going to get interesting, if we run slots, we would expect it to take more time, it's doing comparable stuff to what those two were taking.
However, the memory story should be pretty interesting, let's see what it is, how close is it going to be say to the class versus the named tuple versus the regular tuple.
All right, let's let it go and see what happens.
Timewise, faster than name tuples, that's cool, now let's go look at the memory.
Look at that, 139.3 MB, that's pretty interesting, 139.3 MB, not only does this completely, completely do better than regular classes, it actually does better than named tuples and it even does better than regular tuples so we get the best memory usage using the slots here, and we save 101 MB so that's a huge improvement, now let's go look back our type here.
Remember, regular tuples are very useful but they are very inflexible, they would not be a good stand-in for a class, most of the time.
Named tuples are better, at least they have names for their properties.
So like if I had one here, a, b, c and d and so on, that's cool, but again, they can't have methods and whatnot, on the far other end of the spectrum, we have regular custom classes that are extremely rich, properties, methods, inheritance, overloads and so on, but this one pays a huge price, so what is interesting is we can get basically all those features except the ability to dynamically add fields to instances at runtime after we create them.
if we are willing to give up that thing, we can get huge memory improvements while still keeping all of the flexibility in power of classes.
Now, I want to take a moment and just say do not do this by default, this is not the Pythonic thing to do, this is not how Python is meant to work, it's suppose to work in this nice flexible dynamic way, but understanding how the memory works in these types, and the ability to take control over that and change it, when you need it, when you can say "I can put this one line here", and we need to save 9 GB of RAM on our server, we can do way more processing or manage for your servers, that's a huge win, and it may be worth it.
So, this may or may not be Pythonic, I'll leave that up to you but I thought it was interesting to put it in here into this dictionary section because it makes a big difference and on one hand you say "what you are doing is kind of an abomination against the class", on the other- instead of being forced to use regular tuples, you can actually use rich types and even get better memory usage.
So, you decide, but it's good to know about.
Here is how you do it, you just set a __slots__ and set it to the name of the fields that you are going to use, here we say a, b and c, and henceforth, the only fields that you can have on this immutable thing are a, b and c if you end it __init__ tying to take a "d" and say "self.d =" something else they would crash and say no, you cannot add a "d", it takes "a, b" and "c".
So very strict about the variables it can have but once you do this, it changes the way the memory works behind the scenes for the class.
One more time, use this extremely sparingly but it's a nice power to have if you need it.
|
|
|
show
|
7:38 |
One of the most common actions that we perform at dictionaries is to read values from them and see what they are storing.
So let's look at the variety of ways we can do this in Python.
Here we have a dictionary about a movie, information about how long it was, what its title was, when it was made, things like that.
We are going to go and access things like what was the title, or what was the year and see how we do that.
So let's go over here and try what I am going to call the optimistic style, so we might want to print out the year, so we can come here and I can just say (data['year']) and we should get back this, and let's go ahead and make that a number while we are at it.
So, if I run this you should see at the top "2001", that works great if the value is in there, but if I ask for something like the rating, and there is no rating for this movie, not so good.
so we get KeyError "rating".
So let's comment that out, so that we can get to the rest of our app.
So you might say well, that didn't work out so well for me, let's be a little more careful, pessimistic, let's assume it's going to not work and put a lot of error handling around it, so we could print, we could do basically the same thing here, we could print out the year, we could print out the rating, and we could catch the error and just print it out like this.
Notice the PyCharm thinks "Ooops", it's misspelled, it should be "Oops" apparently.
All right, so let's try this, awesome, so we see "optimistic style", "2001", and if we try to do this, remember, it crashes because our optimism was misplaced, so down here we again, we get the year and instead of crashing, we actually catch the exception, we say oh, there is a KeyError "rating".
All right, so that's one way we can do it, this makes it pretty hard though, there are a lot of times when you want to create concise little expressions, and you want to use the values that come out of these dictionaries, think of a list comprehension or something like that, especially on data science, these are very common and this format just entirely breaks this fluent expression functional flow, so we can do other things instead, now if we want to know for sure whether an item is in the dictionary we can just ask first so we could say "if year is in data", then we'll print data of year.
Similarly, same thing for rating, and it's not just so we can detect it in this case let's print out, "Oh, we didn't find the rating...", all right, let's run and see how that works.
OK, safety first, we checked yes, it was true that year was in there so we want its value printed out, we asked if rating was in there, no it wasn't and so oh we didn't find the rating, is what we found out here.
Now this "safety first style" here lets us check first and then use the data if we are willing to just say "look, I am willing to accept None or sort of a missing value" we can use a different style and I actually like this style, I have started to use it more and more because it lets me test a variety of things all at once.
So down here I can say instead of data bracket where I index in and of course if the value's missing I get a key error, I can say "get", and notice it has a key and a default.
So if we come in here, we can say the key is going to be again year and the default is None, so if there is no year, fine just give us None.
Same thing for rating, so let's run those again.
Like before, we got the year but now instead of a crash, we have some kind of a exception handling or "if...else" block, we just get None and that's actually often quite useful.
Though, sometimes None is not what we want.
So this style up here works well if we are willing to accept None but here we have a year and that's supposed to be a number, what if we would like to have say zero or negative one or something like that for the year if it doesn't exist, we could use our "if...else" block or something like that but actually we can just come down here and say let's get zero if the year isn't there and for the rating, let's suppose we are just going to get a one star, or maybe an empty string or something like that, we'll go with one star for now.
Or maybe so it doesn't look so bad we'll say "3 out of 5 stars", something like that, so if we don't specify rating, we'll get this.
this is a little bit contrived, but at least you'll see how it works.
And we explicitly ask for it but supply an alternative, we get 2001 because of course the year is there, but the rating which is missing just gives us what we would assume to be the default unrated value we'll say that's 3 stars, we could maybe make that empty, or who knows.
This style is really nice, however, it requires that we specify the alternative every single time we call "get" what if we would like whenever somebody uses our dictionary a different default, so there is a thing in collections called "defaultdict", we can import that up at the top and down here we'll have data, we'll just sort of replace data with this defaultdict, so we need to give it a couple of things, one thing we have to give it a callable that will return the default value, not the default value itself but a thing that will create the default value, so we can use a lambda, and we can say when somebody needs to create a default value, let's say "MISSING", so here it looks little funky maybe to you, but this is the function and when you call it, it returns the value missing.
Next, let's make sure that we copy the existing data into this dictionary and then we'll replace it with this default version of itself, let's just print out data to make sure that that's sort of transformation worked.
All right, here is the defaultdict with the lambda function, and the data we expect, beautiful.
So let's try this exact same thing again but avoid supplying any of the values there, if I would run it, we'd expect the year to come out as 2001 as it has every time, and we would expect rating to require whatever the missing value is so it should say "MISSING".
All right, I always make this mistake, even on defaultdicts, when you call "get", you are still going to get the default value, which is the default parameter set to None, the defaultdict behavior comes in, when you access it like this, I almost edited that out but it seems like I make that mistake often and you may make it as well so hopefully it's helpful to see it.
There we go, year is 2001, and instead of crashing, we get "MISSING" for rating.
All right, so that gives you the spectrum of ways to access data from dictionaries, Pythonically in a safe way and you saw that Python gives you many options to control the spectrum of the behavior you want, do you want to make sure it crashes right away if you try to get a value it's missing, fine you can do that, do you want to always supply default value, you can do that, and so on.
So, we started out with this dictionary, and we said let's just try to get the year and rating from it like so, year was totally fine, but rating, not so fine, remember we got the crash, KeyError 'rating', we said OK, well let's try it this way, let's use ".get" and we'd like to specify an alternative value so for year we said the alternative value is going to be zero, and then in this case, we are going to say if you have no rating, please provide -1.
And you can see, because there was a year we got the value, there is no rating, we got -1.
This kind of default is really helpful because then if you know you are going to parse that to an integer, or number, something like that, you can provide a default that's always going to parse, rather than None.
Finally, if we want to set this behavior universally across a given dictionary, we can use defaultdict from the collections module, we specify a function that will return the value when called and here we are passing in the original data to sort of transform the basic dictionary into a defaultdict dictionary.
Now when we access data out of our dictionary, we ask for year, we get the year value because it's there.
If we ask for rating, which is not in there, it's going to call our lambda to supply the default value, that will return missing.
|
|
|
show
|
6:26 |
The Python language has no switch statement.
We have "ifs" and we have "for...in" loops and we have "while" loops and that's about it.
No switch.
But, we'll see that with a dictionary, we can actually simulate a switch statement, so let's look at that in PyCharm.
Let's see what program we have here.
So it starts out by asking which direction presumably do you want to move, we have this little character, his name is Chippy, so Chippy is going to move in a direction, and what we need to do is we are going to ask, provide some options: North, South, East, West, South-West, that kind of thing, and then we are going to parse this into a moves enumeration, you can see we have these various options here, so we are going to focus on this parse method and then later we'll have a quick glance of this move method as well.
So down here, we have the standard parse and what we are going to do is we are going to go through all the possible cases, if you have a "w", we would like you to move West, if you have an "s", we'd like you move South or we'll parse this to a "moves.south" and so on.
So we'll see that this whole segment here can be replaced.
How does that work?
You can replace all these tests for if with basically a key access so let's go over here and we'll call this like parse_dict or something like that, and we can just start printing the values so for "w" we are going to have this one, for "s" we are going to have this one, and so on, let me zoom ahead to build this whole dictionary.
So here we have our dictionary built, so how do we use this to actually replace that "if" statement, we'll just say "return parse_dict.get(text)", so we are actually doing two things here, one we - are looking up the values for each "if" statement by going into the keys here and because we are using "get" rather than indexing directly into it, we are actually providing the default return value that was at the very end of that "if" statement, cool, right?
So let's run it and make sure that this still works, so we want to move South East, it says "You chose: Moves.SouthEast", we print it out to just see what we parse to make sure that that's working, and then Chippy moves South East, yupi, what if he goes North?
Oh, Chippy is moving North, so really cool and clever way to build that switch statement for certain circumstances, when you have this really large set of possibilities.
Theoretically, it can even be faster; so what we have done here is we basically have returned the value given a particular case, but in switch statements, you can also call functions, right?
It's not just a matter of saying "we are going to pick a value" but you can actually say "we are going to run this block of code if this case matches or that block of code if that case matches." So let's move down to our character here and make a change there, so, right now it just prints out the same thing, no matter what direction you move, but what if I wanted to do something like this, "Direction == Moves.North", let's print, "character name moves North with a special hesitation", "else", otherwise we'll just print they move in some direction.
So let's test this.
All right, so if we move South East, "Chippy moves South East", if you move North though, "Chippy moves North with a special hesitation", so could we take this behavior and actually make this into a dictionary switch style statement?
Answer is of course we can, so what does the dictionary look like?
So we are going to need again to define the keys but this time the key is going to actually be the value for direction, and I added a little type annotation here to say this is moves, so this would be like a Moves.North and then we are going to put something here, let me just put None for a minute, so we have one for North and one for South.
So what we need to put here is executable code, we could put a function name that we write somewhere else, or we could just write a lambda, something like this, "Character moves North with the special hesitation", and so on.
Now let's just put these two for a minute, just to see how this idea is going to work, so here we have our action_dict and let's have a default_action that we will use if for some reason we get a move we don't expect.
So here we've got default action "so and so moves quickly to such and such direction." So then, what we can do is I can say the action is equal, I am using a lot of variables here, we could sort of inline this more possibly but trying to be really clear for you, so "action_dict.get" and we are going to give it the direction, but we can also give it the default, action so that if there is no direction method we get this default one and then we can just call "action()" Like so, OK, let's run this.
What directions do we have to move?
We could say North, we should see "Chippy moves North with a special hesitation", awesome, let's go South, "Chippy is going South for the winter!" Now, if we run this and we go South East which is not on our list, "Chippy moves quickly to Moves.Southeast" Cool, right, so basically here is our switch statement, we probably could inline this a little bit better, like for example this probably makes more sense inlining, it's, PEP 8 says we should define this as a "def" if we are going to write it that way, so we can do this, that's a little on a long side, maybe we format it like so, of course, we want to fill this out for all the reasonable actions that we'd like to handle, so this is nice for really short, small bits of executable code, I wouldn't write too much code in these little these lambda expressions here but using this to select values as if you had a bunch of "if" statements, this is really nice, so let's see this concept of dictionaries as switch statements in a graphic.
So here we have basically the code that you just looked at, the moves lookup, we are going to let these specified "w" for West, "e" for East, "s" for South and so on, then we just say "dictionary.get", give it the text we want to switch on, conceptually, and we'll either get one of the values we specified or we get None which is a pretty reasonable response for "Hey, I couldn't parse that value." We saw that these values that go into the dictionary, like in this case Moves.West, it doesn't have to just be a value, it can actually be an executable function as we saw on our character class.
|
|
|
show
|
3:23 |
When I introduced a section on dictionaries I said that JSON and dictionaries are basically isomorphic, there is a one to one mapping between these things.
Let's explore that relationship really quickly here.
So here is some text, just a single string, multiline string here, and it's in the JSON format.
We'd like to take this, which looks extremely like a dictionary in Python, in fact if I take this, say "print(type(movie_json), movie_json)" and I run this, you'll see this is a string.
However, if I say "movie_dictionary = " just copy and paste out of there and indent a little and I do the same thing, this is actually a dictionary and it's pulled this value, I mean, it's basically like you could take the text or JSON and evaluate it, almost, right.
So, that's really cool, but given this text, at runtime, how do I dynamically turn this into JSON because copy and paste static data doesn't make any sense, so we are going to use the JSON module, so "import json", spell correctly, we'll come down here, let's put this down at the bottom for a minute, we'll come over here and we'll say "movie_data ==" we just say "json." Now notice there is a "load", which actually takes a file pointer and a "loads", which loads from the string, so we'll say movie_json, so let's just print this out here.
So we'll do something similar, we'll print the type of movie_data and then let's print out movie_data itself.
So if we run it, we actually successfully parse this JSON text which in reality probably comes somewhere off the web or off the file system, we parse that into a dictionary and here is the dictionary printed back out.
So we could answer questions like "The title is {}.format()" and we'll just say movie_data.get(title), boom.
"The title is Johnny 5".
So, that's a super nice way to go from JSON into Python dictionaries, what about the reverse?
So if I have some dictionary, let's just take the same data and reverse it, we can say so let's just call it movie_json_text_2, and we can get that by just saying "jason.dumps()" and if we give it a dictionary it will dump that out as JSON.
So here and we can just print type of this thing and then print that.
Perfect, dictionary here is the dictionary data, used it to pull some data back, and we want to go the other way to send it across the wire, save it to a file system, we now have a string and it's actually the JSON text here.
So we used the JSON module to make this transformation between JSON and dictionaries, "loads" for strings, "load" for file pointers, and then "dumps" for string, "dump" for file pointers.
So to review in a graphic, here we have "import json" so we can use that module, we have string, which presumably comes off the internet or off the file system, which is a set of JSON text that we want to parse, so we can parse that into an in-memory dictionary saying "loads", now movie_data is a dictionary, if we want to save it back to the file system or otherwise treat it as a string, "json.dumps", boom, done.
|
|
|
|
37:20 |
|
|
show
|
4:13 |
Let's talk about collections, list comprehension, generators and generator expressions.
All of these concepts are extremely central to this idea of Pythonic code, many of them are very unique to Python actually.
The first item we are going to look at is iteration.
We saw that Python does not have a numerical "for" loop, there is no "for(i=0; ;i++)" style loop, you literally work with sequences, you iterate over collections and so on.
There is many built in types that work that way such as lists and dictionaries and so on, but if we had our own type we defined, we might want to be able to iterate over it as well.
Here is the ShoppingCart class, and you can add items to it that you are going to buy later, possibly we'd like to create an API such that you can iterate over the shopping cart and get the items back.
Let's have a look over in PyCharm and see how that goes.
So here is basically the same code and we are defining this thing called the CartItem and it's just really a container for a name and a price, down on line 15 here, we are going to add three items to our cart, a guitar, a cd and an iPhone.
What if we wanted to loop over our cart?
Maybe it works right now, let's just try, so if we want to write the code "for item in cart:", maybe we'll just print this out, so we'll print, let's do the name and we'll do the price here, we'll do a little format so we'll say "item.name, item.price".
And let's do a little header here, so items in your cart.
You can see that PyCharm is warning us we are kind of going down a bad path here, so it's like "this is not going to work", but let's go ahead and give it a try, just to see what the error is.
Boom, ShoppingCart object is not iterable.
OK, so we'd like to write this code but how do we do it?
the ability to add iteration to a type is based on the Python data model, which all the dunder methods comprise.
So we can come up here and add this particular one, we can say "def __iter__" and form this method we have to return iterator object, which has a length and next.
If we just want to loop over the items as they are, we can leverage the underlined collection class itself and it knows how to create one of these so we could just say "self.items.__iter__" go back down here, PyCharm is happy, that's a good sign, let's see if it works.
Boom, "items in your cart: guitar, cd, iPhone".
Beautiful.
What if we wanted to have a little more control than just exposing the underline structure, or underline item here, what if we wanted to say "sort these and then hand them back"?
We can come over here and we could say "sorted_items = sorted" and we could pass self.items, and we could pass a key selector, we could say here is a lambda that given an item is going to return item.price, and then we can return sorted_items.__iter__ now you can see we have out items but sorted, not necessarily the same way they were stored before and we could even go and say I'd like the negative price here, so now we have the most expensive ones first.
So you might think that this is fairly distasteful here and I don't really like it either, we are going to talk more later about generators, but if you are familiar with the yield keyword, we could write something like this: "for i in sorted items yield i", we could write this code as well, and this would do basically the same thing, it returns the generator rather than list but that's fine.
So take your pick, we'll talk more about yield later.
OK, we saw that in order to add iteration to our shopping cart, we just need to add a __iter__ method here rather than just exposing the underline self.items we are actually exposing a sorted version of it as a generator.
So now we come over here we add some items into it and if you want, we can do a "for...in" loop over our cart point out the items as you saw and we can grab once we have them, the name and the price and print those out.
So it's super easy to add custom iterations to your type and building on this Python data model with the dunder methods sometimes called magic methods is a very Pythonic thing to do.
|
|
|
show
|
3:21 |
Next, let's talk about testing for containment and various sequences If you want to look for an item in a set, in a dictionary, in a list, those types of things, and you are new to Python you might look for some kind of find or index of type of method on the type itself.
But in Python, we have a special keyword to do this test, over here in PyCharm we have a list, a set and a dictionary and the way we test for containment in them all the same, so if we'd run it, you can see we are just printing out these values and if you look at the numbers, you probably recognize them as the Fibonacci sequence up to 34 anyway or five here where I had to write them out, so what we are going to do is we are going to parse out a number gathered from the user, and then we are going to test whether this is in the set.
So, here we'll just do a few "if" tests and maybe we can do this as a tertiary sort of expression, so we can say "print" like so, so we are going to say we'll print out something is in the set and then we'll do out "if" test, we'll say "if n is in nums_list" and then maybe say a list here, keep the same order, otherwise we'll say "not in list".
All right, so the test here is "n in nums_list", all right, so this actually goes through and it searches the elements in it and it does a comparison not on index but by value, and then it'll tell you "yes or no it's here", then we could do the same thing as you'll see for the set and we could also do it for the dictionary.
All right, let's run it and figure it out, here it says enter a number to test for the small Fibonacci set or a sequence and let's say well, say 21, 21 is in the list, 21 is in the set, but because I was lazy and didn't write them all out, 21 is not in the dictionary; let's try again, how about 1, it should be in all of them yes, it's in.
So, "if item in container", this even works for strings, so if we had some text here like "Why did the multithreaded chicken cross the street?" do you know?
Well it depends on when you ask it, you'll always get a different answer, this time we are going to get "Other side to the get".
So I could ask a question "word", so here we'll say something, we'll do this not the tertiary way, we can say something like this, "if word in text: print such and such is in such and such", there, so we could say ask user for a word, they type it in, we can do the same "in" test for a string, let's try, first look for 7 which should not be there, now I'll look for chicken, chicken is in the "Why did the multithreaded chicken cross the street", let's try it again, this time we'll enter 2 and here we'll put a cat.
Right, so cat I don't believe appears in here.
Cat is not in this string.
All right, so let's see that in a graphic, so here we are just going to work with dictionaries as you saw, it's basically the same across the three types of containers we worked with.
Here we could try to directly index into this dictionary and say I want the thing with key 2 but as we saw in other examples, this could give us a KeyError, if it's not there, so we might want to do this sort of check first style so we could say "if 2 is in the dictionary", then we can safely access it because we know it's not going to KeyError.
|
|
|
show
|
7:22 |
When I think about idioms that are particularly Pythonic, slicing has got to be one of those.
Slicing lets you take things like strings and lists and so on, and even much more advanced items as we'll see and create very concise syntax and very understandable syntax subsets of these items.
So, let's go look at this in code.
So here I have a main method, it's calling a Fibonacci function and it returns set of Fibonacci numbers that are less than 200, it returns these as a list, in the beginning I just print them out so you can see what we would have to work with, so here are our Fibonacci numbers, and suppose we want the first five, well there is a variety of ways we could do this, we could do a little loop and gather them up and break out of it after we get to five and so on, but in Python, we can go to our list, and we can just say: "I would like to go from the zeroth item, up to but not including the fifth item", something like this, and then if I print first five, you'll see we actually get the first five.
Now, we could write it like this, but Python has a lot of conventions around slicing, so if you are going to start at the beginning you can say just ":5" and it says go from the beginning to five.
So we should get the same output, and we do.
Down here, if we want to actually go from the second to the seventh item, we'll say, just print it out like this, let's be clear what we mean here, we mean the thing at index 2 up to and including the thing at index 7.
So we'll say 2 and that would give us just the item index 2 or the third item up to, now for slices, it does not include the value put here so you want to put one higher, let's just verify this, OK so if we count by index 0, 1, 2 so then 2 is here, 3, 4, 5, 6 7th index item is 21, so we did get exactly what we were looking for using 2 to 8.
We can do more interesting stuff, we can also go and get the "n", so I could say nums and I could put something here, we could start by saying "len of nums", and then this value, this is not so amazing but we could say like -3 here, and this will kind of work, so here we've got the last 3, great, we could use our convention that I pointed out before, that if you are at the beginning or the end, you can omit it, so we could write it like this, also still get the last three, but in true Pythonic fashion, we could do better than that.
We can say we'd like to start 3 items back and then go to the end.
Beautiful, that way we don't even care, have to look or know what the length is, so that's really nice.
So let's put this under the absolutely Pythonic "last 3" version.
All of this stuff is working within memory lists and we could do with strings and other types as well, but the title was "Slicing collections and more", so how far can we take this more - well, this is pretty interesting - from the database, if we look over here in this slicing support file, we are not going to cover SQLAlchemy in detail in this course, but we've got a class that we are mapping to a SQLAlchemy database as an id an x y and a value, these values I believe are between 0 and 1, OK and it stores this into a local slicing_db.sqlite file and it connects to it, we are going to import this session_factory here to actually create a connection to the database.
Now, if we look at the database, OK there is nothing over here, right now, but if we go to our project and we drop this in here, you can see we have all this data and the part that we are going to look at is this value, so we would like to use slicing to get the top 3 highest values out of this database, OK, so let's see how that works.
Up at the top, we are importing session_factory and Measurement, so let's create a session I'll say "session_factory", we'll call that, and at the end let's remember to close the session, we'll create a query here, we'll say "session.query of Measurement", and we want to say "filter(Measurement.value) is greater than .9", we are going to order by Measurement.value.desc().
OK, so this is great, maybe we could just come over here and do a ".all" to get this back as a list and then I could just print out the query, I am not sure it's really a query but whatever, if we run this, you realize what are the challenges - you have to spell "filter" correctly, here we go, once that works, you can see we have a bunch of these back from the database and we could even order it.
Let's go over here to our engine and turn on tracing, what this will do is this will actually show us the SQL commands going against our database, so in the end down here you can see basically "SELECT * FROM measurements ORDER by", you know, where the value is greater than .9, order by the value descending, OK.
Oops, here is the select part, so this is pretty cool, how does slicing have anything to do with this, all right, so if let's take away this all, if I want just the top 3 measurements, I can actually use slicing to say "give me a subset of the results from the database", all right, so I could say something like this: "top 3 = " and I could say "query, go from the beginning up to 3" and that would give me the top 3 records, let's just print those out really quick, so look at this, "SELECT * FROM table WHERE value is this, ORDER BY that, LIMIT and OFFSET and the two values we're passing are .9 for the WHERE clause and then 3 for the LIMIT and 0 for the OFFSET, so first 3 ORDER by descending", so those are going to be the top 3, now we could actually go a little farther and say well, what we are really looking for is just the measurements, so I could say "m.value for m in query up to 3" like that and then I'll actually show just the values.
So those are the highest 3 values and you can see they are very high and descending, how amazing is that?
So, the reason I took the time to do this SQLAlchemy example is slicing is cool and at first it feels like OK, this is a cool way to work with like lists and strings, but slicing is so much more than that, slicing is deeply integrated into many of the APIs and packages that you are going to work with, and so while this is really cool, this right here, this is super amazing and this really shows the deep power in a breath of slicing.
So let's see this in a graphic.
All right, so here is our numbers again that we want the values at index 2 to 7 or we would say 2:8 remember, the last item is not included, we want the last 3, the best way to do that would be "I want to go back 3 and then the end", so -3:end, that worked perfectly, we could even create a database query and get to say "give me the top 3 measurements :3 so 0 to 3" and you can see that actual query generator is "SELECT * FROM Measurements WHERE measurement...
da da da da LIMIT 3 OFFSET 0".
Amazing.
|
|
|
show
|
8:09 |
Here is a function called classic_fibonacci and what you do is you pass a limit to it and it will compute all the Fibonacci numbers up to that limit.
Notice we have a list called "nums" and it does all the work, fills this list up and once it's finally done, it gives you all the numbers.
Well, what if you want the first million Fibonacci, what if you need the first 5 million Fibonacci numbers, how long will this method take to run?
What if you don't know how many you need, what if you want to start looking at them and you say well, I am looking for the time when I am going to the Fibonacci numbers and the second one is a prime number the third one is the cube of the first one in the sequence, who knows when that is, you are just looking through and you are going to decide "oh, now it matches, now I have got enough of these".
What if you were looking through this and you said "I am going to ask for 5 million Fibonacci numbers" and it was really the 5 millionth and first, right, maybe you just gave up.
So we are going to look at a different way to write exactly the same code that doesn't have these limitations, allows the consumers to process as much of these actually infinite series as it needs and yet does this in a very much on demand, high performance way.
This concept is called generators and it has this keyword called yield.
So let's look at this in code.
So, here is that same function, we can run it, it shows you the first few numbers in the Fibonacci sequence we are passing a limit here, we are passing a 100 so we want just the first set of Fibonacci numbers less than a 100.
So this is fine, but let's see if we can do better.
Before we move on, let's actually debug this a little bit.
So I am going to put a break point here, we are going to step into this, all right, so here we are and let's step into this method, and now we are stepping along, stepping along, and notice we are going through the list, you can see up here it actually shows you the list being built, it shows you the numbers so PyCharm is really cool in that sense, you can see the list growing, but notice we are the whole time staying here until we get to the limit of 100 which happens pretty soon here, right now, and then, we are going through them and processing you can "m" is the various values here.
So that's fine for small numbers, but what like I said, in the beginning, what if we don't know what the upper bound is?
Or what if we have to put a really huge number here, what do you think happens to the memory consumption as that number grows, obviously we have to gather all the numbers that preceded it and hold them in memory all at once and then you get the answer.
So Python has this really cool keyword called "yield", and let's come down here and let's call this a generator_fibonacci, so we are going to do a few things, that if you have seen this before, you know it's pretty straightforward, if you've not seen this, it'll probably blow your mind.
All right, so what we are going to do is we are going to say instead of having this limit, we would like to work on the infinite series, now if I just run this code, two things will happen, first of all it's going to crash in a hurry, even if for some reason it wouldn't crash, if we had like infinite memory, it will still never return, right?
It's just going to keep adding this infinite series but of course it's going to run out of memory.
So in Python, we can do something both cleaner and better here, so what we can do is we can use this yield keyword, and yield is like return but instead of returning from the method, it just says "hey, I want to create a collection or a sequence and here is one of the items, and here is one of the items", so we'll yield "current".
So, that's cool, so that's going to actually generate - continue to yield the items, you might wonder well, how we ever get a value out of it?
So let's go find out.
So we are going to do this, now if I run this, it won't crash or anything, it will just keep spitting up numbers, scrolling to the right until it kind of goes crazy, so this is an infinite sequence but as a consumer of the infinite sequence, I can decide "OK, I've had enough".
So what I will say here is let's say "if m is greater than 100", we can use the same test as we have on line 36, we can just break out of our loop, all right, so let's run this, we should see the same output, we do, right, classic and generator have the same output but if we go into debugger here, it's going to be all sorts of different, all right, so we step in, here we are in generator_fibonacci just like we were before and here is our "while True", now watch what happens as soon as we get the current, which is 1 and we say "yield", immediately we are back here, we printed it and now look where we return into that loop, we just kind of resume the method back here, see there is this back and forth, I'll do this a few times, notice now we are going to jump back into this one and that current is 3 and next is 5, this is like a state machine that remembers where it left off and can be resumed, but even though it's an infinite sequence, we don't generate all of them, it's more like on demand as you pull items out of it it will compute them, so only as much as you pull, you have to pay in terms of computation.
The other really cool benefit is nowhere are we adding this to a list so nowhere are we using, basically nowhere are we storing more than one item at memory at a time so memory is not a problem in this situation.
So these generators are really cool and all you have to do is use the yield keyword.
If you compared against classic_fibonacci, not only is it better performance, more flexible, generates all the numbers and so on, it's actually shorter and once you get your mind around yield, it's actually easier to understand.
So that's cool, we can also take down here, we can create a something like an even_generator() and if I were to pass some kind of set here, some kind of number generator like this, I could say "for n in numbers, if n % 2 == 0" our standard even test, we will say "yield n".
So given any set of numbers, whether this is a list or a generator, it doesn't matter, it doesn't care, it's going to pull the even ones out and then down here, I can define a method called even_fibonacci and we'll say something like this: "for n in even_generator()", and then we can give it generator_fibonacci and we can say "yield from this".
So this will let us compose these things so we can actually create pipelines from one to the next.
So let's run our even Fibonacci through here and we should get only the even numbers that are also coming from the Fibonacci set and remember, this is an infinite sequence because we are starting out with the innermost bit, an infinite sequence, which itself is a generator that will take as many items are there and pass them back.
But because we don't actually do the work on this part until we pull on it, and we don't do the work on this part until we pull on it, it goes something like this, pull here, that means go pull this, which pulls on this, which will pull on this piece, one item at a time and then when we decide down here we are done, we'll break out.
So look at this, we have the even Fibonacci numbers, and there is not many so 2, 8, and 144.
Here they are, brilliant.
If you want more, we can get more.
Want up to 10 000, no problem, there they are, 10 000; up to a million, there they are up to a million.
Boom, like that.
All right, so let's look at this in a graphic, remember, we already talked about our algorithm here, it's a perfect implementation of Fibonacci but it has the limitations where you have to say how many you want before you actually get a chance to look at the numbers, and you can't look at too many or you'll run out of memory if for some reason you had infinite memory, you'd run out of time.
We can switch to a simpler version using the yield keyword create this as a generator and it actually does no work until you start pulling on the generator.
More of what we saw that you can write multiple generators and compose them in a pipeline style which is really awesome especially in things like data science.
|
|
|
show
|
3:41 |
So we've seen how powerful and amazing the yield keyword is to build these generators.
In Python 3, there is actually a new feature that makes working with generators as well as recursive functions even better.
So over here we have some code and what it's going to do is it's going to go to some root directory here I just grabbed the transcripts from my other class, Python Jumpstart By Building Ten Apps, and the transcripts are here in these demos folder, and we want to just process through those, so I've written this function called get_files() and I give it a root directory, and it returns using yield the generator that we can iterate over and print them out.
So this is pretty straightforward, we are going to go to a directory, this will be the top level directory, and we'll say "for each item I'd like to look at it", let's build up it's full path and ask: "is it a file, or is it a directory?", so if it's s file we'll say "yeah, I found one of the files in this directory, here go loop over this", but if it is itself a directory, well let's just hold off on that for a minute.
So here if I run it you can see on my Mac I have this .DS_store thing and then I have this txt file and then that's that.
So not many files.
But it turns out there is subdirectories in here and maybe I want to look inside them if I had a function that could look inside a folder, and tell you what was in it, tell you the files that are in it, that would be awesome, I could use that, right?
Well, what do I have right here, boom, so what we can do is we can use a concept called recursion and if you are used to recursion this makes perfect sense, but if you are not, it's quite interesting and sort of mind bending, so the idea is from within this function we are going to call the same function but with possibly, this time certainly, with different parameters, so we are going to work our way down the directory tree until there are no more subdirectories then we will stop calling our function but as long as there are subdirectories, we are going to be calling it like this, Now this returns a generator of files and technically it will return like a tree of generators, of files so how do I get the files out?
Well, I could write this, "for f in files, get files" and then I could say "yield f" and so this is just the idea of recursion, there is no special feature here, but let's just verify it works.
Boom, here you go, so you can see in app 10 I've got a couple of transcripts, in the conclusion I've got a couple of transcripts, there is quite a few files that were in subdirectories here.
Lovely.
And notice we actually are printing the directory as well, I'll turn that off for a minute.
So those are just the files.
So like I said, this is straight up recursion, and this is kind of not-so-great, we'd like to just say hey here are a bunch of items in a generator and I would like to make all of those items part of my sequence, so in Python 3, we can do this, we can say instead of just yield we can say "yield from get_files" and full_item and this is basically replacing that loop above so we can do it in kind of a inline sequence way, let's try it again, we should get exactly the same output, boom, we do, beautiful, so "yield from", super helpful when you are doing recursion or you want to just grab a bunch of items from some kind of generator or set and throw them into your current set that you are trying to generate.
So here you can see we are calling "get items", it's a generator because it's using the yield keyword and we are also calling it recursively and we are able to simplify that recursion using "yield from".
So remember, this is a Python 3 only feature and in fact, it was introduced in Python 3.3 so it doesn't even work in the early versions of Python 3.
That said, if you are working in 3.3 or above, it's a really cool way to simplify generators.
|
|
|
show
|
6:22 |
Let's continue our exploration of generators, we saw that we can create generator functions using the yield keyword, we saw Python 3.3 added "yield from" to work with recursive generators and things like that - combining generators, those were all functions, so we were able to transform the way the function worked but what about loops?
What about things that are smaller, little bits of code like what we have on the screen here, we've got some kind of iterable set called measurements, we want to loop over it and we want to find all the ones that have some value over 70, we want to gather those up, so just like the drawbacks our Fibonacci sequence where we pass the limit had before, this loop has similar problem, but the yield keyword won't help us, so let's see what will.
So here we have some code, we've created a named tuple, named Measurement, it's got an id, an x y coordinate and a value.
So think of this like a 3 by 3 grid, here where we have numbers or measurements like temperature or something around there.
So if we want to find all the locations that have some kind of high value or actually just look at what their measurements were, we could go through like this, we could write a loop, first we could create a list to gather the measurements, the high values, we loop over them, we do some kind of test and we add them up.
All right, so that's OK, but it's not great.
However, let's just look at the rest of the app really quickly before we are done, we are going to come up with this, these numbers in a variety of ways, we want to print them all out here, so if we just run it you can see here is the ones we got through the loop, so I am calling this C-style but it's really any procedural programming way and of course this blocks while this runs, now we can come down here we can take this code and we can do something a little bit different, we can create what's called a list comprehension, the result is going to be exactly the same, the execution also will be basically exactly the same, but we can take this and more or less inline what we have here.
Now it looks like you are going to start out and we are just going to define a list, but what in fact what we are going to do is we are going to define this thing called the comprehension that will loop over values and build up a list.
So the first thing you put is the values that are going to go onto the list, you have to imagine in the next statement, the next line you are going to have some kind of variables, so I am going to say "m" again and the "m" is going to have a value, I'll say for "m in measurements", just like above, and we'll say "if m.value is greater than or equal to 70", so high measurements are 1 to high measurements 2 are the same, this is more declarative, so this is pretty cool but they both sort of block and build this list, so in a lot of ways they are very similar, the benefit here is this can be passed as part of an expression, whereas this is like separate code suite that you have to stop and then run, you couldn't like pass this as an argument to a method, but like I say: "This you can, you can compose them and so on." So let's see the results are the same, of course they are, excellent, so this executes and turns into a list but we talked about the generators, that let us only pull out the items as we pull or we iterate over the generator.
So that's really cool, now we can do basically the same thing over here, if you have square braces that means a list comprehension execute and return a list.
If you have parenthesis but you put basically the same thing inside, you create a generator that you can then iterate over, this is just like writing a method with the yield keyword.
So, if we just try to print out high measurements gen, you'll see that we actually just get a generator, not a bunch of values because they hasn't actually executed, hasn't pulled on it.
So, in order to actually display the results we do this, wrap it in a list, make it generate something that we can then print and then there it is, these list comprehensions are cool, there is other types of comprehensions as well, all right, the generators, the yield, and that's most interesting I suppose, but we can also create a dictionary suppose instead of just having the values, I'd like to say "given an id of a measurement, what is its value?", so we can come down here, we can do something like this, or so, but instead of just passing the value here, I will say "key:value", so I would say "m.id:m.value".
Now if I run that, you can see here is the id value and id, here is some crazy id value is 73, but it is these values that you can look them up now by key, not super helpful when you have 4 values or 5 whatever that is, but if you had hundreds of thousands, we saw how amazing that could be, so this actually generates a dictionary because it's "key:value" for item in some set.
Well, for item in some collection.
Now we can also create just the distinct values if you look down here you'll notice 90 is repeated 3 times and if we just want to know what are the actual measurements, like was there a measurement of 90, was there a measurement of 73, and so on, the ideal structure for that would be set.
So we can use almost the same syntax as the dictionary comprehension here, but instead of saying "key:value" we just put an item here, and if we use curly braces, and one value - not a "key:value" - that becomes a set.
And of course, the set is distinct items, so here is a wide variety of ways to replace standard C-style looping and gathering behavior into lists, replace it with the generators, replace it with dictionaries and replace it with sets, all of these constructs are highly Pythonic and used often especially when you are creating these pipelines and passing one to the next.
All right, let's look at the core concept here, as a graphic.
So we saw we have our direct loop style or C-procedural style code create a list, loop over a bunch of items, if they match some test we add them to our list.
But, just like taking this type of algorithm and replacing it with yield worked really well in a function, we can do the same thing with loops inline using generator expressions.
So, it's much of the same mechanics but the execution is vastly different so we say parenthesis for generator and then the value we want to get and then we loop over the item with the "for...in" loop and then we do a test with an "if" clause, there you have it, these generators are super useful, study them, you use them in a lot of places.
|
|
|
show
|
4:12 |
Now let's look at determining how many items are in a generator.
So if I have something like this, high measurements, and it's I am getting the value, looping over some collection called measurements, and I am doing a test, well, I actually have a really hard time knowing how many are in there, let's go look at that in PyCharm to see why.
So this is basically the same code that we used to talk about generator expressions in the first place, this time, this is set actually, fixed that, so here we have our high values, now if I try to print out the "len" of them, get the length, you can see PyCharm is already trying to tell me I am going down a bad path, but let's see what happens anyway.
Boom, object or type generator has no length, what might be wrong with getting the length, well it could be infinite, and it might take forever to determine that, but most importantly this is not going to work, all right?
So we are not going to do that because it crashes, we could do something like this, we could say "create a list and pass into it the high values in them", if you pass a collection here, it will iterate overall the items and put it in the list and then I could print "len of list".
However, one of the beautiful things with generators is if even if there is a million items here, we only hold one in memory ever, well if we do this, we kind of undo that, we now have one million of them in memory but let's just see that it works, ta da, 4, OK, 4, that's cool, so we can use a combination of some really cool things, so if I had something like, let me just do something simple here, I'll say "sum" and say given any set of numbers, I could add them up, so those 3 numbers should have 7, we should see 7 down here, perfect, OK, so we can use sum to give it some kind of collection here, let me separate these, so we can kind of isolate them, count here and we'll say "count equals this", right, so we could add this up using sum, we could leverage this, along with another chained comprehension, so what do I want to put in here, for every item I see in here I would like to add one, because what I want to know is how many items not what is some of the values, so I could sum up the high values here, OK, now this actually broke, now this is worth knowing why did this break, so we have 4 and 0, obviously it should at least be 4 right, these are not 0 numbers that we saw, but here is the thing, unlike lists, once you run through a generator, it's done, you have to recreate it, so basically this, the fact that I did this used up the generator in a sense, you can only use them once, if you want to do it again you recreate it, if that's not going to work for you, create a list comprehension instead.
There you go, so 375, there is not 375 items in there, there is 4 so what I want to do is somehow in the best, most efficient possible way go through this list and say "for every time I find an item, give me one", so what I can do is I can create another generator, I can say "give me the number 1 for n in high values".
OK, so what we are going to do is we are going to through and say "every time you find a value, I don't care, I am not going to use this value", let's say 1, and that's going to add it up, now remember, it's very Pythonic to say "if I am not going to use a value, use this indicator say underscore", like here is a variable that has to come out and be stored somewhere but by saying underscore I have no any intention of using it, so we should get the answer 4.
Beautiful, so here we have our generator, you saw generators don't have a length, we can't use that, if we try to throw them into a list or something along those lines, that's not good because that undoes all the benefits of the generator, it loads everything in a memory all at once, so we can use this cool combination of the sum method and a chained generator expression, so the chained generator expression is "give me one for every time you find an item in high measurements", which is itself a generator, and then if we sum up that set, we actually get the number of items in the generator.
Remember, just be really careful it's used up after this, so if you want to run it again, you need to either recreate it by having the 5 lines above again, or turn into a list where you can reuse it over and over.
|
|
|
|
35:45 |
|
|
show
|
1:18 |
Our next category of Pythonic concepts and tips is going to be around functions and methods.
Python is a multi-paradigm programming language, we can write procedural code, we could write object-oriented code, we could write functional code and with things like decorators we can even write aspect-oriented code.
Python's functional support is very strong, you'll see the functions and methods are first class symbols and citizens in Python and they are highly flexible and powerful.
When you define a function or method with a "def" keyword, you're really instantiating a function object and you can pass that object around just like you can pass a number or a string or an instance of a class.
You'll see that those function objects can even be changed at runtime you could dynamically add a field to a function just by saying "function.value=something".
Not saying that you should do that, but just considering the flexibility, right.
Functions even allow you create things called closures, both inline functions as well as lambda expressions, that's a very powerful programming technique often used in places like Javascript for data hiding and encapsulation.
And finally with things like lambda expressions we can even define small inline methods as little bits of executable code that we can pass around in super concise and composable ways.
|
|
|
show
|
7:05 |
The first highly Pythonic concept that we are going to talk about are these things called lambda expressions.
These are like small, inline methods that you can pass around, chain together and build larger expressions from.
Let's look at the idea of using functions as a parameter in the first place.
So, here we have find_special_numbers, now this function is just going to go through some set of numbers and it's kind of hokey I know, but it's going to loop through a bunch of items, in this case the numbers between 0 and 10 and it's going to apply our selector, so a special selector is a function that takes a number and returns a boolean.
So we can call the function, pass it a number and it will say this number should appear in our list or maybe it won't.
Now this method might look for even numbers, it might look for Fibonacci numbers, it might look for prime numbers, I don't know.
That's the point, we can pass whatever type of function we want in here and the selection part will be done by that function whereas the gathering and looping part will be done here.
So let's look at this idea in Python.
So, down below we have our find_special_numbers, just like you saw in the slides, and I've written this other function called check_for_odd, right, you can see it's doing the standard modular check_for_odd numbers; so we can come up here, we can combine these two things together, like so, we can say "for n in find_special_numbers" and this takes some kind of a selector, so I can say check_for_odd.
Now, PyCharm automatically tries to call this function, but I don't want to call it, I want to just pass it, all right, we'll see that is I take this and I actually print out this here, maybe I'll even do the type for you, do the type and then the actual value of it, we'll see that this comes out as a type of function and a particular function pointer to a particular type of function.
So just like any reference, we can pass it here maybe we want the first 50 numbers, we'll just print those out.
And let's print them all in one line so that you can see them, so we use a separator of comma to just comma-separate these values, so let's run this.
Perfect, so you can see we've got our prime numbers here, including the first 50 prime numbers that we were looking for.
And also see what we printed out our type of check_for_odd, we've got the type as a function and it's a particular function "check_for_odd at that address".
So that's cool too.
Now, this works fine, but writing this check_for_odd function down here every time I want to be able to pass a function around, this is kind of- well odd, so it works fine, but it separates the implementation from where we are using it, and if the implementation is really simple, it can clutter up your namespace with all sorts of little functions and it can move where you are using them from where you are defining them so it's a little harder to understand what's going on.
Let's take this basically the same idea here, and maybe so it doesn't shoot all the way off the screen we'll lower that number, and we can come down here and we can say "I want to do the same thing but this time I want to check for numbers divisible by 6 and I want to use a lambda", so let me just write it on a separate line first.
Call it "check = " and then we could pass the check just so it's more clear, so with the lambda expression I would like to just say given some number "i", I would like to somehow say "return i % 6 == 0", right, now this obviously is not the right syntax, given this, I don't know, this value goes here and just sort of passes this little bit of code, so in Python the way we say - we are defining lambdas you say lambda and then the arguments, the parameters, and you say colon is your separator as you normally would, every lambda has a little expression of value it creates and it returns so you don't say the return value, so there, this is our lambda expression, now if we run it, it should work.
Perfect, here are divisible by 6 numbers, so it works, but PyCharm here is saying: "you know, not so much, PEP 8 says don't define lambdas outside of their actual use as pointers", rather we should do a little miniature "def" here, so let's inline this as it's kind of meant to be used.
There, so we can just take our lambda expression and pass it as a parameter, and that's what lambdas are for, you can create these little expressions that you can chain together pass these parameters and so on.
So we should get exactly the same behavior if we run it.
And we do.
Cool, so if we have to just come up with these little bits of code, here and pass them around, lambdas are beautiful for this, let's look at another example.
So here I have a bunch of words, and I would like to have them sorted, I'd like to have them sorted in a way that regular people would say "yes, those words are sorted alphabetically." So one way you might say "let's give it a shot" is we could just come over here and say "words.sort()".
Now, whether I use sort or I could say sort it, these will generate sorted list that I can then go and work with, the difference is this changes the underline list of words whereas this returns a new copy of it that is sorted, so it doesn't really matter, we'll go with this one for now.
So let's try to sort like so and see what we get.
OK, 'CPython', 'Please', 'a' and 'changes,' - these look sorted, and those look sorted, but as a group they don't look sorted to me.
That's because right now the sort is case sensitive, OK.
Well, what do we do, are we just out of luck, do we have to write our own sort algorithm?
No, of course not, so what's cool, let's comment this out, because it almost works but not quite.
In both versions of sort, they let you specify a key selector, and what this key selector is, is it's a function that given one of the items, in this case a word, we can return something that we'll actually use as the sorting value, the comparison value, so we could put a function here, but I am going to define a lambda expression, so I'll say "lambda w for word goes to" - well, if we just put it like this - "w" it will do the same sort but I actually want to sort without regard to the case, so let's do this, let's say lower any time you want to compare word, do not compare the actual word, compare the lower case version, we could use upper and so on.
Let's try it.
Now look at that, that looks sorted, doesn't it?
And look how incredibly easy this is, "key=lambda w: w.lower()" That shows you some of the power of lambda expressions in Python.
Let's look at that in a graphic.
So here again we have our find_special_numbers, we also saw the same situation applies to built-ins like lists and so on, so we want to pass some kind of selector and we could write a special method somewhere using "def method name da da da" and pass it but if it's a small little test, it makes much more sense to do this as an inline lambda expression, like so.
So we just write "lambda, arguments, goes to, return value" basically.
If there is no arguments, you just say "lambda:", you get multiple parameters like any other method as well.
Using lambda expressions is a very Pythonic thing to do.
|
|
|
show
|
7:29 |
In programming, there is several philosophies on how you deal with errors.
One hand, you could look at all the various cases, check all the return values and do a lot of tests before you take any action, to try your best to make sure that action will be successful.
This type of error handling is popular in languages that are not great at supporting exceptions, such as C.
Languages that do support exceptions lean more towards what you might consider an optimistic style of API, where they try things and if something goes wrong they will catch the errors and deal with it.
So let's look at how this shows up in Python.
All right, so we have this little support file and in here it has a couple of things, support module, it has a download file and if you attempt to download a file you need a bunch of things to line up in your favor, you need the network to be connected, you need the download URL to in theory be set, you need the DNS to be active, and you need to actually have access to the file you are trying to download.
Over here, we can just say "well let's just try to download this file and see what we get", let's run it.
Oh, cool, we download some data and it was a binary array saying "cool", but what if something goes wrong, let's go over here and fiddle with it, like let's say, let's turn off the network, now how is this going to work if we run.
Not so amazing, "ConnectionResetError("Cannot connect to the network")", oh, OK well, if we were coming from a C language, a C-style language or these languages that typically don't have great exception support, even if they do have exception support, often it's not well used as an idiomatic way of programming, think C++ for example, you will see lots of people write algorithms that look like this, we'll say oh we've got to make sure the network is working so we'll say "if s.check_network()", maybe we'll at least put some guarding clause so we don't have that nested thing we spoke about earlier, so we'll print out something like "cannot download, no network".
And we'll just bail, so let's run this again, excellent, OK.
So, "cannot download, no network", we didn't crash we just caught this error, now there is some other cases we should check, we can check the DNS, we can also check the URL.
OK, still network is turned off, let's go turn that back on, we will turn off, the let's see, the DNS now, oh "can't download, no DNS", so here is the question, if I look at this code, is this code going to deal with all the possible errors?
Well, it turns out in several ways no, no it's not, so first of all, we forgot to check this one, say that's true, so we thought we did all the tests it looks like we did a lot of tests at least, we are running and crash, still no go, because we don't have permission to that file and it turns out if we are doing real network I/O deep down within Python there is all sorts of exceptions that can be raised, so the message, the takeaways basically even if you try to write this code they still deal with all the cases you need to put this into a "try...except" block.
OK, well if you are going to go and put into a "try...except" block, why don't you just skip all of this stuff, use the programming model that's called "it's easier to ask for forgiveness than permission", try it, if it fails we'll say "well, sorry, catch, handle the error", because it's kind of the code we are going to have to write anyway, so let's write a better version, a more Pythonic version here, so we are going to say "run_with_checks()" and let's first turn everything back on, so this download works, so down here we have run with error handling, it's going to crash, well, if I had an error with crash, because we have no error handling, so let's go over here and we'll put a "try...except" block, so we'll say we want to catch exception and maybe even get the details like so, and we'll print "Cannot download...", something like this.
So, let's go ahead and run it, remember the download is working right now, so this will just do the same thing, perfect, it does, let's go mess with this, let's go say turn off the network, and run it.
"Cannot download, ConnectionResetError", "Cannot connect to network", OK, that's not great, let's put this back on but it didn't crash, we did catch it, that's cool, let's say go over here to the permission one "Cannot download: Permission error", "Cannot access resource (permission denied)".
This is cool, this is much more Pythonic than what we have above here, right, one thing we are not doing is we are not doing anything different based on errors, now technically we are displaying a message that varies by error to the user but often you can do different things based on the type of whatever you've got.
We might want to deal with DNS and network errors differently than we would deal with say a permission issue, which also might be dealt with differently than if we had like the download URL not set.
So let's go down here and write this last version, so let's just see the types of errors we get, so I can get a permission error, maybe I want to run some particular code if there is a permission error so we could, say, add another except block here "PermissionError as pe" and then I could we don't even necessarily need the details, we just need the time, so we could print something like "Cannot download, you don't have permission...".
Theoretically, you would do something different here, we also saw that there were connection errors, here like so, we can print "Cannot download, problem with network"; and maybe we could put the details in here like this, "Cannot download, you don't have permission...", so excellent, this code is running, now if we have a different type of error, say there is a problem with the network "Cannot download, Problem with network: Cannot connect".
What about DNS - "problem with network, no DNS".
So there are two Pythonic takeaways here, one - this is how you do error handling in Python, much less like this, although there are places where this makes sense, it's not the primary way of doing it.
And if you are creating APIs, don't depend on the return value and lots of checks, instead just try do evaporation and raise errors properly, make sure that you raise different types of errors so that we can do different types of responses based on those errors.
So here is what you call a "look before you leap style of programming", it's popular in C and C++ and those types of languages, you do a bunch of checks, and you try to test every possible case and then you perform the operation and hopefully you have tested everything you need to and it doesn't just crash on you right.
In Python, we typically don't write code like this, instead, we write code like this, we just assume that it's going to work so we'll just do the most cleanest, simplest, straightforward way of downloading file, how do you want to do that?
"s.download_file()", boom, done, but, something goes wrong, we put it into "try...except" block, handle the error and we can even use different error types, most specific to most general, to deal with specific errors, like for example here we are dealing with the class of network errors that have to do with DNS and basic network connectivity.
This is called "it's easier to ask for forgiveness than permission" style of programming.
And this is more Pythonic than the prior version.
|
|
|
show
|
2:42 |
In Python, there is no function or method overloading.
Here we have two methods called simple on this class, now the first one takes no parameters, the second one takes a details parameter, in some languages, these would be two distinct methods and based on the particular signature you are trying to use, the compiler would select one or the other.
This does not exist in Python, let's look at it in an example.
Here we have the same basic code and we are creating what I call the Sample class, that really doesn't mean anything, and we are going to call a simple method on it, notice we have this kind, we have this kind.
PyCharm is giving us a little bit of clue that something is going wrong here, you can see it's highlighting the second simple on line 6 but let's go ahead and run it and just see what happens.
So look, the first one where we pass some details, this actually worked, I call this simple with details and it said "Some details." However the second one didn't work, "simple() is missing 1 required parameter: 'details'", so what's going on here?
It turns out there can only be one method called "simple" on this class, and so when we define the second one we basically eject this one from the class, we just overwrite it in a dictionary that the key "simple" now means something different, and so even though PyCharm is little bit freaked out by this here because it were doing it wrong above, did catch that error, this is the one that is actually not going to work because as far as this class is concerned, there is no method "simple" that takes no parameters, oh look, in the subsequent sections on how Python deals with this, because this kind of flexibility is super powerful and Python does support it, it just doesn't support it in the traditional method overloading way that you might be familiar with coming from C++, Java, C# and so on.
In a graphic, here it is.
Here is our class, we have the two methods, the top method is being overwritten or ejected by the bottom one, these could just as well be functions and not methods it would have the same effect, but what is really important to notice is when I ran the code, it wasn't the fact the I was redefining "simple" that was actually causing the runtime problem, this code as it's on the screen here, this will run perfectly fine it just won't do what you think, so be very careful here.
So for example, if we create the "Sample" class, we call a "simple" method with details, the last one in our list that is going to work correctly, but the bottom one crashes because it no longer exists, basically.
Now, there is nothing specifically Pythonic about this, but this lays out the problem the next 3 or 4 lectures are going to show us Pythonic ways to solve this problem that do not have to do with method overloading and signature matching.
|
|
|
show
|
3:39 |
The first Pythonic technique that we can use to address this what you might call a shortcoming, at least a different way of programming around method overloading is with default values.
Let's have a look.
Here in PyCharm we have some simple method called display_greeting, it's completely contrived but it'll totally work for our purposes.
You give it a name, you give it a greeting, so the name might be Jeff, the greeting might be "Good morning" and it will actually say it over and over and over so you can get really excited and say "Good morning Jeff, Good morning Jeff, Good morning Jeff", and in fact this one will do that 3 times, this one on the other hand will just say "Good day Michael", one time.
However, there is a problem with these down here, we might like to write code like this, we might just like to say well, let's just greet Mark, and there might be some way to write code that there is a default greeting to be given like "Hello", and the number of times might be 1 so like if we don't pass the greeting and the number of times, we'd like to just say "Hello Mark", one time.
But if we say "Mark" and "Good afternoon" we'd like it to say "Good afternoon Mark" one time.
Of course we can specify all the details and say "Good afternoon Mark" twice.
How do we go about this in Python?
Well, we use default values.
First of all, it's not going to love it the way it is, you can see PyCharm's indicating issues and if we'd run it you will find them, the first part worked just fine, "Good morning Jeff" and then did that 3 times, the little error snuck in between there, and then it said "Good day Michael" and then we started hitting the trouble.
Click here and it will take you right to the line of trouble, yeah that's the one we expected.
So we can actually go up here and instead of having different signatures, we can have default values, so if we'd like to have default greeting we can come over here and we can say, right in line, "Hello".
So if we wanted to say Hello- name, if you don't specify it, then we can do it this way.
Now, this would almost fix this line, except for we still need to deal with times and the default values have to go after all the non-default values, so let's set this to 1, that seemed reasonable; now, this actually fixes all of these errors, let's go.
Perfect, look, if this one here "Hello Mark", this one said "Good afternoon Mark" one time, this one said "Good afternoon Mark" two times, like so.
Finally with these default values we can actually put them in any order we want, here we don't say the name of them we just say "Good afternoon and two", we use them as positional values but I could say something like this, I could say greeting is "Yo!", name is "Michael" and times is 4.
So we can put these in any order we want using keyword arguments and we get "Yo Michael" 4 times.
More importantly, this lets us two things like skip over, let me keep this here for you, more importantly his lets us skip over some of the default values, so here I can say name is Michael, skip over greeting and use its default "Hello" and then let's just say 2 times here.
So they should say "Hello Michael" 2 times at the end.
"Hello Michael", 2 times at the end.
All right, so in Python default values play a really important role in doing what method overloading based on signature might have done in other circumstances.
We'll see some more Pythonic ways to deal with this as well, some other functional techniques we can use.
So, specifying default values here, lets us perform what in languages like C# and C++ often are done through signature overloading and having multiple methods that are distinguished by signature.
However, there is a warning here, so for these default values there are some extremely serious gotchas and certain circumstances will look at those at the end.
|
|
|
show
|
2:21 |
Another way to add flexibility to functions is to allow you to pass a variable number or maybe more correctly an arbitrary number of parameters to it.
So let's look at that in this case of the silly function I wrote called biggest, so "biggest" will take two numbers, any really two comparables and tell you which one is bigger, so like biggest of 1 and 7, surprise, it's 7.
Let's go look at this in code.
Here we have the same thing as on our slides, if we run this, you can see still 7 is bigger than 1, hasn't changed.
Cool, but what if we want to have more than 1 argument, what if we wanted to somehow, let's go in and write the code what if we wanted to say the biggest of 1 and 7 and 42 and 99 and -1 and 11; what if I wanted to write that code?
Well, if I try it's obviously not going to love it because it says it took two positional parameters I was given 6, not a good deal, so we can use convention here in Python called *args, so star, args is the convention, * (star) is the keyword or the language feature, that says this thing is going to accept an arbitrary number of parameters, the x means first it means you have to supply at least one but you may supply more, so let's first of all just print out what is this args and what is it and let's comment that out for a moment, if I try this again, you can see that I was given a tuple 7, 42 and so on, if we look here, that's the remainder after the x.
So let's go write the code that actually does the biggest part here, there, that seems like a reasonable implementation, we'll start out assuming the one that we have is the biggest and we'll go through everything that was passed to us as many arguments, zero or more that you give us and we'll check, well is this one bigger, if it is we'll set that one to be the result.
So what should the answer be at the end?
99 of course.
Boom, and it is.
So here is another Pythonic way to add flexibility to your methods, in a graphic, we saw we had this limited version that could compare two things, using *args we were able to upgrade it to take an arbitrary number of items and we saw that the thing that's passed in the args is actually a tuple and we just loop over it or do whatever you want to do with the tuple of additional parameters.
|
|
|
show
|
3:42 |
The next Pythonic concept I want to explore is the relationship between dictionaries and keyword arguments.
Over here we have the same function that we explored previously, it takes 3 arguments, a name, a greeting and a number of times to greet that person with that greeting.
So we could say "Michael", I'd like to say "Hello" to Michael 3 times, something like that.
And we saw that we could use keyword arguments even to change the order or to skip over top some of the default values, so here we can say greeting and then name, using the keyword arguments and skip the times.
So let's just run this really quick to see how it works, "Hey, you are out of order Michael!", brilliant.
So suppose that I had a dictionary instead, something like this, where we have a name a greeting and times and the keys in the dictionary correspond to the keyword arguments that we are able to use in the method, so there is a way to take this dictionary and turn it into a function call or rather parameters to a function call via keyword arguments, so we could say display_greeting() and we can unpack the dictionary saying **, so it says instead of pass it as a dictionary, unpack it a keyword arguments where you have the names are the keys and the values are the values.
Let's see how that works.
All right, so "Hey you are out of order, Michael!" from up here and then we said "Ted, long time no see", do that 6 times.
That's excellent.
Now this concept of ** representing a transformation of a dictionary works in both directions as well, so up here I could say **kwagrs, now this is much like the *args we had before, that was allowing us to pass an arbitrary number of additional parameters, this lets us pass an arbitrary number of additional keywords so if we come over here now, and let's go and just print out what kwargs, we'll say, "kwargs =" so if we'd run it, you can see it's empty but it looks kind of like a dictionary and in fact it is a dictionary.
How do we use this?
Let's come over here and let's wrap this a little bit, let's say additional=2, mode=7.
So now, these do not correspond to any parameters named or otherwise in our display greeting, they will be gathered up into this additional kwargs here and pass along and we can do whatever we want with it, we can check for the existence of mode and do something with that, theoretically.
All right, let's see how this runs.
So now we pass our items: the greeting, the name, the times, we've also got these two additional arguments to pass in here, so in functions, you'll see this **name and the convention is for that name to be kwargs but it doesn't have to be, you'll see this serving two roles, either this takes keyword arguments and turns them into a dictionary in this case, or the reverse, it takes a dictionary and turns it into keyword arguments.
Let's see that in a graphic.
So here we have the same function, you can see we have the **kwargs, here you can see we are passing the greeting, the name the times as they are via its default value, we are passing another=2 and you can see we get our greeting and kwargs is a dictionary with another as it's one of its keys.
In the reverse, we can take a dictionary and use the **dictionary name or a **pointer to unpack the dictionary as a set of keyword arguments to a method.
|
|
|
show
|
7:29 |
We've seen the power of default values and methods.
But they can have a dark side that you need to watch out for.
It's not hard to avoid, but you need to be aware of it.
Let's see this first in code then we'll come back and look at the graphic.
Over here I have a method.
It does a couple of things and it kind of gives us a hint on what's going on by naming the methods "bad" and "good", if we have an add_items_bad and add_items_good, now the good part is not yet good, so don't expect it to behave well.
Now let's just look at "bad" real quick.
What we'd like to be able to do is come over here and pass in a name, some number of times and add that name to the list however many times we set.
Again, this is a very cheesy example but it's pretty simple and it will make it totally understandable what's happening.
So we want the behavior to be like this, either you provide us a list that already exists and then we'll add to that list or if you don't give us a list, we'll create a brand new list for you using a default value here and we'll add to that and we'll pass it back.
Sounds like it's going to be great, right?
So, let's come over here and comment some of these out, so we are going to start out and we are going to add the item "a" 3 times.
So our list here should be "a, a, a," and then we are going to call this again and we are going to pass "a" in first we are going to use the default value then we are going to pass it and it should onto that list add two more "b"s, so in the end, our list here should be "a, a, a, b, b." Let's see that that's the case.
First time "a, a, a" was created as part of the default value, and then "a, a, a, b, b." OK, so this is what you would expect, there is nothing weird going on here, let's continue though, and here you'll see something go completely wrong.
So this first time our expectation was: we don't supply list, great, the method will create it for us and give it to us, populated.
Here, we are going to do the same thing, we worked with "a", we are now done with it, we want to create a new one called "d", "d" for danger, we are going to create a new one called "d" and we are going to add "d" to it 4 times, so what you would expect is basically that, these characters.
But you are going to see that that is not what we get, let's try it.
We get "a, a, a", "a, a, a, b, b", right?
Now this is what we expected but what the heck is that?
Well, if I had to guess, I would say it reused the list a that it gave us on line 2 and in fact, that's exactly what happened, we can even come down here we can say let's compare, if I say I'd like to print out the id of "a", basically the pointer address, and the id(d), if those are the same value, we have a problem, we can even print "id(a) == id(b)" because it's going to be kind of a big number, who wants to compare those.
So our expectation was every time we did a call like this we got a new list, empty, that was "d".
We got a new list, empty, and it would be filled up, otherwise we specify an existing one but that's not what happened.
Oh dear, those two lists are the same and of course that's why they look like we added the "d" to the first list, so let's go look at the code down here and see why that happens.
Well, it all has to do with when is this default value created, is the default value created every time the function is called?
Or is it created when the function is built - when the function is defined?
And you know, see PyCharm here it knows something is up it's coloring this in a way that says "no, no" this is probably not what you want, so if we hover this it says the default argument is mutable and yet there is only one of them that ever exists, so if it's only one of them and it can be changed every time the method is called, this is not a good situation.
So it's fine to have these singleton immutable things, but this one is mutable and this could be a custom type, this could be all sorts of things, in this case it's just a list.
So how do we deal with it, how do we get a add_items_good so we don't run into this problem?
Let's go and hit and just uncomment all these down here, run it and you see we have the same problem, even put my test down here.
Right, so you can see we have the same problem, obviously because we have the same code, but let's fix it, so the way you fix it when you have a mutable type as a default value is you create it every time so you need some kind of indicator that this is not set, so we are going to say None, we'll say "if list is None", remember we check for None with "is", not "equals", although "equals" would work, this is better, we'll say "lst = new list", so this achieves what we were hoping this would achieve for us up here but actually didn't.
Now, it's worth noting that we could say "if", you might be tempted to say "if not lst", then we’re going to do this thing, but that might not be exactly what you want, if they were to pass the list and it was empty, like this but they pass it in, this would still be False, remember the truthiness of sequences, so then we would recreate it and we would add, possibly to a pointer, that they never grab back, because they thought they passed it in, so we are not going to do "if not list", we'll do "if list is None", we'll recreate it.
Now, let's run the code, the bottom wants you to work the way we expected it, look, PyCharm is not angry with us any more, because this is an immutable singleton, let's go.
All right, so obviously bad news, perfect, this is what we were looking for - "a" - this was a default one created, then we had some more values to it, to the existing one, then we are going to call the function again with default, and we get brand new different list they are not the same.
So be aware of this possibility where you have mutable default arguments.
Here I have colored list red because we are using a mutable default argument, now what we have learned is that this default argument is created once per process, basically, so this is a shared list for everyone who calls this function without passing a value for list but just rather uses the default, this is not going to be the behavior you are looking for.
So you saw the first two lines below this method here, list one, this worked perfectly, then we tried to create a second list calling add_items_bad with the default value, and we got some very bizzare behavior, in fact what we saw was list_2 and list_1 were in fact the same list.
So how do we fix it, we put some kind of indicator here that we need to create the list, in this case we said if they pass None for the list, or they don't pass anything, we'll create the list for them, so we check if list is None, we create it, and then that way every time we call this function we get a new individual dedicated default list.
Oh wait, there is one more thing, I almost forgot and this is really cool; remember I said notice PyCharm sees the error and it highlights it and says "oh no, this is not going to work out for you probably, this is not what you think it is", right?
But I ignored this little part they said Alt+Enter fixes it, so Alt+Enter in PyCharm will do all sorts of fix-ups and automatic transformations, if it knows there is something, a way you can do something better you can hit Alt+Enter and often it will do it better.
So I can come over here and hit Alt+Enter, and it will say "we would like to replace the mutable default argument", boom, just like that.
Alt+Enter, fixed.
And what did it do- it did exactly the thing we did, below.
All right, that was the thing I forgot to show you.
|
|
|
|
19:14 |
|
|
show
|
1:48 |
Python is often referred to as a programming language and ecosystem with batteries included, and on one level that means it has a really rich standard library.
Things like the JSON module that's built-in and so on.
It also means looking at the larger ecosystem all the 80 000 packages on PyPi, things like that, so in this section we are going to focus on the Python idioms around packages, modules, importing them, creating them, those kinds of things.
I want to give you just a little bit inspiration before we get to the technical details so if I come over here and run Python 3, and I go type in "import", I could say "import json" things like that, and then I could say "json.dumps" given a dictionary and so on, right, "json.dumps", here a is 1 and boom, we have JSON, but we could also import all sorts of things, we could go to PyPi install some packages and import them for example I could "import requests", because I've installed that somewhere, to capture this idea of how amazing packages are, we have this concept of "import antigravity", so what happens if I import antigravity?
Well something pretty awesome, it pulls up this xkcd about why Python is awesome because you can import anything so here I'll just read it to you really quick, so we have this guy up here he is totally flying and his friend says, "Dude, how are you flying?" "Python, I just learned it last night everything is so simple, hello world is just print "hello world!"" "I don't know man, dynamic typing?
White space?", "Come on, join us, programming is fun again, it's a whole new world up here" "But how are you flying?" "I just typed import antigravity", "That's it?" "Well I also sampled everything in the medicine cabinet for comparison, but I think it's the Python".
This is the feeling you should have as you think about packages and modules and all the stuff that you can do, let's talk about the idioms about consuming all these amazing packages.
|
|
|
show
|
5:53 |
Let's talk about import statements.
Over here we have a variety of things being used that should come out of modules that are mostly in the standard library but some of them we build ourselves.
So you can see we're using the system module, we say "sys.versioninfo.major" so this should print out "3" the way we have our system setup right now, of course you can see there is an error here and we should come over here and say "import sys".
So this is one way we can do this, and this is certainly considered Pythonic, it's using namespaces, right, so "sys.", we know where this version info is coming from, and remember, namespaces, those are one honking great idea, let's do more of those.
OK, cool, so we are doing more of those here, now sometimes, you don't want to have to say the namespace or the module name here, and especially this really long like "SQLAlchemy.orm.ext.declaration.", this is maybe a little bit long, but sys, sys is great.
However, if you would like to use a type over here we can say "import os" and we could come over here and we could say "os.path", but we'd rather just say path, so instead we'll say "from os import path".
We can do it like this and this is also considered very Pythonic, there is a shortcut way, we could get hold of, here we are using the stats module, statistics technically, we'll rename it, so we could get hold of median, the mode, the mean and all those things, if we said "from statistics import", rather than naming them, the correct way would be to say median mean and so on, name them, but we could say, let’s leave this here and I'll comment it out, we could just say you know, I'll just use everything, that's cool thanks.
Well, you can see all these 3 lit up this is considered to be not Pythonic at all, let me show you why.
So we have this, suppose we want to use median and mean from the statistics module, and let me go ahead and import this as well, so we'll say "import statistics as stats", so here if we want and if we had something really long, like I said "SQLAlchemy.orm.declarative.
da da da", we could rename it, so here we could say "import statistics as stats", and then just say "stats.", so kind of taking over the namespace, to greatly simplify it.
Suppose mode here is not the statistics mode, but we want to set the mode of operation of our program, so we have kind of a crazily named file here, beware_the_trade_imbalance support file and in there, there is a mode function, you can see "def mode", it prints, that really didn't do anything, but under one condition it prints "Mode set to DEFAULT" or "Mode set to ADVANCED".
So when we say "mode" down here, this is actually the mode we want to use, so I can come over here and say OK, cool, so I'll say "from..." we want to import mode.
Now, PyCharm just because of this weird naming convention I had here, thinks this is a private thing, so let me just tell it: "Don't make this look like an error for us." Because normally that would maybe mean "protected" but it doesn't in this case.
So, now all of our code should run, we print out the major version, the current path, the median of those numbers, again, that should be the same median, then the mean, so the median, median, mean, and just like we would expect we have our mode set to advanced.
So our mode is set to advanced.
The None is coming from, let me actually, just this doesn't return the value in that case we wrote.
OK, so that's the way it worked, but suppose instead of doing this Pythonic style of importing without the namespace, I said you know, I just don't want to worry about it, let me, I want to have a bunch, let's just get them all, so we can go like this.
However, even though I was not using the mode from statistics, this imports mode from statistics, flat out, and all the other ones, I am not sure how many are in there but many of them.
Now notice, PyCharm knows something is amiss here.
This has gone gray and says, "you are not really using this mode", that should be a warning that something is wrong, so if I remember this said "mode set to ADVANCED", now If I run it, mode is seven, what happened?
We imported mode and then we reimported mode, which replaced its definition in this module.
So mode is gone.
All right, we never intended to use mode from statistics, we just wanted to be lazy and not import those two separately, this is bad, don't do this.
Notice when I comment this out, this gets enabled again and let's do one more thing, notice how this got some errors and these are undefined, and I did type it up here but let me remove it for a minute and just show you the PyCharm can fix this, so if I go over here I can hit Alt+Enter and it will say, now because I have the stats up here already it knows, it's trying to help too much, so if I come over here and I hit Alt+Enter, it'll say "import statistics.median" and I hit this, great, and again Alt+Enter, you can see, it's doing the Pythonic way of doing the import here for us, perfect.
And of course, let's put our stats back because we were confusing PyCharm there.
Let's see this in a graphic.
So namespaces are great, "import sys", that was cool, importing bare items by name, that's fine, "from os import path", we could rename or shorten our namespaces, "import statistics as stats", maybe it doesn't make sense in this case, but I will give you some examples where it does, and we also saw that we have to be very careful with wild card imports, "import *", because the two lines above, we are trying to get mode from our custom package and mean and median from stats and if we wanted to get lazy and say "forget mean, median, and we should write *", we would blast away our custom packages mode definition.
|
|
|
show
|
5:21 |
One entirely non-obvious convention that you quickly learn when you get into Python, is this __main__ concept, for controlling when you should execute your code as a program and when your code should behave as a library or a module.
Let's look at this simple example.
So here we have two modules.
We have the one that is suppose to run as a program, over here, and we have another one which defines a method, a variable and a class that we are going to use, and you can see we are importing this or redefining it to something reasonable and we are saying things like "the variable we got out of s", so s.method/class/variable, there they are, so the variable we've got out of here is whatever, when we run, let's comment this out for just a second, if I go and run this, you can see it printed out this code it said the variable value is such and such, great, the variable value is a variable.
So it looks like we imported this successfully, we worked with some of its data, we could use methods and classes and you know, everything.
But what is this deal down here, well, this is something you are going to see often in Python and you don't have to call this method "main", you can call it "run", call it whatever, but basically we are saying: "Define this function up here and in the case where __name__ is main, run this." We'll just print out __name__ really quick, so we'll print this.
We run it, OK it is __main__, let's go over here, this one, and we'll say print to the same thing, print __name__.
So the name of this is this great long support module thing, so we are going to run it, well, first of all, when I import this, it should trigger this to go.
So the name is, this full name here "chapter 6 packages, blah blah blah", not a nice name, it wasn't really built to be reused, it was built to be descriptive about what part of the class it fits in, but watch this, if I go and run this, let's make this a little more obvious, let's say- so here we have the support library name and let's put this as main app name and we'll run this first, so here the support library name is what you expect, main app name is __main__, that's not what it says up here but we'll talk about why that is, but if I run the support library, its name is now main.
So here is the convention: If the thing that is being executed directly, the module or the script that has been executed directly regardless of what its real name is, it's called __main__.
Everything that is imported up here like so, when it's not the target but it's just being imported, it's given its module name, basically the name without the py extension.
So, what we do in Python is we use this to only conditionally execute code, suppose over here and this support library we had something like this, we said, we wanted to ask a question, "while True", we'll say "age = input("How old are you?
")", like so, and then we'll convert that to an int, and let's go over here and say age=0, let's say "while age is equal or less than 0", OK?
What happens here if I go and run this?
I would like to see I'm going to import this and just use this variable, so let's try, let's try to run this one.
OK, so it tells us what the library- wait a minute, why are we getting "How old are you?", let's say 0,0,7, oh, so that ran and then our code ran, let's make this a little more obvious, let's go up here and say print "About to import support lib", I'll say "done importing", so we try and you can see about import support lib and then we are just like stuck here, because when you import a module, you are literally just executing it top to bottom, executing this defines a class, executing that defines a method, executing that defines a variable, but this, this is not what we are going to run, we are just trying to expose our variables and methods and so on, this might be if this was actually the script, so you can see this is a problem.
7 now we are done importing, now this runs, so we could come down here and we could say, we could use our convention, we could say "if __name__ == '__main__'", only in that case, only when this is running as a program do we do this, when we do that, this won't run, if we import it.
So let's try again, about to import, printed out the name here, this is not __main__, done importing library, we've got our variable.
But if we go over here and run this one, support library name is now __main__, "How old are you?" I'm 7, awesome.
So here is what that convention is all about, the "__name__ == '__main__'" is all about disambiguating the case where your script is being used as a library, as a module in somebody else's code, or it's being executed as the target.
This is so common that PyCharm has a shortcut for you, you just type main tab and it expands it up.
we saw that when we import a module its name is just the name of whatever the file is, so in this case it's going to be support for the top class when we import it in the bottom.
However, if it were executed, it would have a different name, it would be "__name__ == '__main__'" and that allows you to disambiguate the times when your script is being run as a program and when it's being reused for its functionality.
|
|
|
show
|
2:33 |
Let's talk about isolating your dependencies and your versions for your external packages, from all the other Python projects on your OS.
Here we are in the terminal, and I am in this directory here that I have a bunch of Python environments, and I'd like to create a new Python installation basically, for a new web app I am going to work on, or any kind of app, really, I'd like to be able to control the version of Python is there as well as the packages that are installed and their versions independent from everything else on my system.
So I can use virtual environments for this, in Python 3, we have a "venv" command and we can also use the virtual environment's external package, we can also use the virtual environment's external package, which works with all versions of Python.
So I'll go and use that here but they work exactly the same.
So I want to create a directory here that's going to contain my Python environment so I'll say "virtual"- let's make sure we have the right one first, "virtualenv", OK, this is going to be the one for Python 3.5, so good, so I'm going to say this, and I'm going to give it a folder, let's just say sample_web_env, so we know it's an environment, not the web app itself.
Spelling is hard, so we can see it's created a version of Python here based on Python 3.5 and installed the necessary tools, basically that we need to add more packages.
So, now if I say "which pip", it doesn't yet have this environment active, the creation of the environment doesn't activate it, so the next thing we need to do is say dot(.), so the first dot(.) means apply this to this shell rather than a separate one for the execution, and we'll go in the "sample...
bin activate", we run this, now our prompt changes and more importantly, if we ask the same question - "which pip" - now it's this one, if we ask "which Python", it's this one.
OK, so we're ready to use that, let's say pip list to see what we have installed, we just have those 3 that were installed there so we could go install something like I could say "pip install requests", and it's gone and downloaded, now if I ask what's installed, I just have this.
So I can have version 2.10.0 of request regardless of whatever else is installed, upgraded, downgraded, in the rest of my OS.
All right, let's go and upgrade pip.
OK, so here is our sample environment, we'll be using this in the next section.
|
|
|
show
|
3:39 |
One of the challenges of deploying your code, your set of Python scripts, to run on other systems, is to communicate exactly what you depend upon, so that you make sure that that system has the right things installed.
We saw that virtual environments allow you to control this, but how do you state it, how do you help someone grabbing your library or your app know what they've got to install?
Let's look at that.
Over here I have a little app, it's going to do some downloading and it's using 3 packages, now these would be interspersed throughout your app of course, right, but in this case, we just have them listed here.
So we are using a request to download some the homepage in Google, show the status code, imagine somewhere else using records for SQL, over here we are using user accounts and correct hashing with passlib and so on.
So if I run this in PyCharm, on my system, it works great, I've got 200 back from Google.
Let's imagine I was going to take the same code and run it somewhere else; to simulate running it on another machine, let me go to that virtual environment we created before and I'll just activate it, so I'll say ".user/screencaster/Python_environments" this is what I created, I'll say "activate", OK the prompt changes, now if I say "pip list", you'll see I don't have all the things we need, I do have requests but I don't have records or passlib, let me see what happens if I try to run that program.
So we are going to run it and oh, that didn't go so well, I guess we needed records, we would go "pip install records" and we tried again, we'd see passlib and that's because- and that would be actually the easy case because it's all in one file, but normally, it would be spread out so eventually you would get to some action that import a module that "oh, well that crashes too" because there is some other missing piece.
So how do we solve this?
It's quite simple, we can come over here and I would put whatever my code is, I want to run, I would give it a requirements.txt.
and in here, the format is super simple, you just list the names, one per line, of the packages you depend upon, so if I copy this and I come back over to my "other system" where I have, remember, I am using this pip from here, if I say "pip install -r" for requirements file and I give it that, it's going to look at all the requirements we've specified, download them, and make sure the system is ready to roll.
As long as I have kept that requirements file, up to date with what my app actually uses, we're good.
And PyCharm if we are working in certain types of environments, actually is really good about managing that for us, if it sees you work inside of a package like say a pyramid web app, and it sees you using some external package, that is not listed in your setup install requirements it'll actually automatically put them there for you.
OK, so now if we say "pip list", this looks like a much better chance, let's try running our little app again, we should just see 200 as it talks to Google and gets good response code, server says: 200.
So that's the requirements.txt file, add all of your requirements to it, just one package name per line and then "pip install -r requirements.txt".
In a graphic, our app is using some external modules, or external packages, here we are just showing requests, in order for this script to run at all, we are going to need a request installed on the system that's going to be running it.
How do we communicate that?
Well, we have our requirements.txt that lists out our various requirements, then we "pip install -r", give it the requirements text file and boom, problem solved.
|
|
|
|
16:30 |
|
|
show
|
6:18 |
Let's talk about the Python idioms on classes and objects.
And let's start in the construction of classes, how do you build them up, how do you add fields and to a lesser degree when we get farther along, methods.
So here I have a class defined called NotSoPythonicPet.
And we are going to do several non-Pythonic things to it but let's start up by giving this pet a way to set a name and to set an age so that we can ask it, hey pet, what is your name, what is your age.
So we can come over here and this is very non-Pythonic so don't do this, we can come over here and we can say "set_name" and give it a name here, and say "self.name = name".
OK, that's great and we could do the same thing for age so now we can set the name and we can set the age.
Now, there is nothing technically wrong with this code, we shouldn't do this but technically it's not wrong, these are just warnings saying "don't do" what we are doing here because it's not Pythonic, OK, so but we can come over here and say "cow.set_name()" and let's call it Betsy, and we could set its age and how old is this cow, 7.
OK, so let's run this, make sure everything hangs together, we have a pet.
Now this little string over right here, this is not the best description of our not-so-Pythonic cow, because we could say "hey, this is a pet, it's name is Betsy, it's age is 7", so why don't we do that.
So a pet whose name is {} and age is {}.
So now we have pet whose name is whatever the name is and the age is whatever the age is, so let's try this.
Great we have a pet whose name is Betsy and age is 7.
Now, technically, you can set fields on these types anywhere you want, within them, out here, I can also say "cow.happiness = 11", it's a very happy cow, probably one from those California milk commercials, and we could even incorporate the happiness up here and run it, and great, it's happy.
What's wrong with this?
Obviously, we should not be doing this.
Why?
Because, what if we forget to set the name for example, bam.
Sorry, this pet has no attribute called name, that's unfortunate, isn't it.
And even if we called all the methods, how are you suppose to know that you've got to do this, right?
This is really a terrible way to create classes, let's go over here and turn, we'll get rid of all of these, we'll just comment those out.
Forget this happiness bit for a minute, that was just playing around, OK, so how should we do it?
Of course, we probably want to pass this to the initializer, if we did want to have the ability to set a name and set an age, we could leave this here and say "self.name = None", and "age = None", or maybe "age = 0", as it's unset, something like this.
So run, that doesn't give us a great answer, but at least in the __init__ we know all the moving parts of our class, of our type.
So, this is not, well, this type has a name field, if and only if you happen to call this other method but before that it doesn't, right, this is a terrible way to write code, so don't do this.
And if you feel you must do something like this, at least initialize these to somewhere empty.
But I am going to go ahead and say "let's not do this", let's instead...
I'll leave this commented out for you, for the code you download, let's instead say "you have to supply a name and age to create this class", to create an object of this class, and we come down here to say "self.name = name" or in PyCharm you just hit Alt+Enter, and it will do that for you, and Alt+Enter and it will do that for you, and it does it of course, the way we are recommending.
But now, we've got to supply a name and an age or it's going to crash as you can see, and Betsy's back.
Let me show you one other way of adding fields to a class that works really well and is very common.
So remember, in our slicing example we were over here doing this query against this measurement type, let's look at that measurement class, for a minute.
This is a SQLAlchemy ORM-based class and it's mapped into our database, via SQLAlchemy, so basically there is a measurement table, corresponds to this class, now notice, here we are not using the __init__ we are actually defining the type by adding these class level fields, so we've got id, x, y and value, over here, notice we can say things like "cow.name" and that works fine, it runs fine, but we can't say NotSoPythonicPet.name Now, PyCharm finds it here but it probably shouldn't because if you run it, this type has no name, obviously.
This is an instance level property, you can think that this is kind of a static level type of thing, as a static field from other languages if you will, so over here, if we write it like this, we get to write code like this, so here is how we actually wrote our query to do this, I want to create a "query(Measurement)", "filtering(Measurement.value > .9)", order_by(measurement.value.desc()), things like that.
OK, so this is another very common way to define fields of our class that I think is Pythonic, if you want them to be type level, if you want them to be only instance level, this is the way to do it.
Here we have our NotSoPythonicPet, and it's doing a couple of things right and a couple of things wrong.
First of all it has a "self.age = age", "self.name = name", in the __init__, that's good, but when we call "get_name" it happens to set another field, another attribute that only exists after you call "get_name" that turns out to be a really bad idea.
And we can get the age back by saying "object.get_age" we should define our fields only in the __init__ or in the more static style that I showed you, a SQLAlchemy, and we should never create new fields outside of __init__ based on some behavior that makes it very hard to understand if and when those fields will be there.
|
|
|
show
|
5:27 |
Encapsulation and data hiding is a key building block for object-oriented design.
And Python, being a very object-oriented language, or at least having great support for object-oriented programming, of course, has ways to do this.
But I would say it's less Pythonic to focus heavily on these ideas, things like private variables, and whatnot with inside classes or protected variables that only derived classes can see, things like this.
But let's look at it anyway.
So, over here we have a class called PetSnake, and you can give it a name and you can give it an age, and you can supply this protected value but it builds it up as you create it and possibly these changes over time, right, this is a great simplification of anything you might really use.
And, like before, we have this string overwrite, where we can print out some information about this.
So here we can say "Here is my pet snake:", I want her called Slide, it's 6 years old, and we can just print it out, that will call this method, we can also access its values directly here, so let's just run this.
Great, here is my pet snake, age 6, looks like it has an age and a name backwards but that's fine, and the protection level here, perfect.
There is nothing wrong with this class, it seems fine to me, but what if we wanted the age and the name to be read-only?
Once you have created a snake, you can't change its name, once you've created a snake, you can't change its age, other than possibly having some way to like give it a birthday or something like that.
First of all, let me switch these, because this is kind of bugging me, this is backwards, so in Python, there is a way to do this and let's work with this protected value, let's suppose that we would like this to be accessible to derive classes but we want to indicate to the consumers of it, "hey you probably shouldn't be messing with it", so let's just, before we change it, let's print it out over here, so here we'll print it out and see everything is fine, if you look at the warnings form PyCharm, no warnings.
So the way that you indicate something should not be consumed outside of the class or more generally outside modules, sort of externally is to say "_" as the prefix.
So now if I say this, notice, this goes away, obviously, because it doesn't exist, but we can put it back, that's fine, this goes away because it doesn't exist, we can put it back, but now we have this warning and PyCharm is saying: "Access to a protected member such and such of class you probably shouldn't be doing this unless you know what you are doing." However, this is just a warning, it still works.
Notice here we are reading the name and the age but we just as well could, and we are going to say "py.name = py.name.upper()", something like that, so now we have Slide, so we are actually changing the type, OK and maybe I'll change this print statement order as well here we go, SLIDE and SLIDE, capital.
So what if we don't want this to be possible, we want read-only access to this and we'd have to provide a way to get to it which, we'll get to later.
So the way you do that in Python is you use double underscores, and of course down here, those names changed, let me put this back for just a second, if we really want to make this change we can hit Ctrl+T and do double underscore and change it everywhere Ctrl+T to save me some typing and be safer, of course.
You can see it changes everywhere but down here PyCharm is like "not so sure this is going to work well for you", unresolved reference, well, maybe it's just hiding from us, maybe it's saying you know, you really shouldn't access this, we are going to tell you that it's not there.
If I say "py." and the only reason it thinks the name is there is because we are doing this line, if I take this line away, there is no name, and it thought that line was creating the thing called __name which it would have, if we set it, you can see those don't show up.
OK, so now let's run it and see what happens.
Boom, PetSnake has no thing called __name and yet if I hide this, it does seem to have __name, so what is going on here?
So you really can't access it by name here, so let's look, so we'll look inside of type and say "what methods and fields does it have?" with this thing called dir, so I can "dir(py)" and ask: "What basically features do you have?" It'll show us all the various things here, so if we come over and we look for, here is our protected value, let's go and add just one normal value, so I'll just say "self.normal = True", so here at the end is our normal value, here is our protected one so we can't get to it, we are just told "you probably shouldn't".
So here we are saying "self.__age", "self.__name" and that seems to work, but it's actually got this rewritten name, where it's rewritten based on the type.
So technically, you could come over here and copy this out and access this, and it certainly wouldn't look like what's written up here and it would tell you "you know, you probably should stay away from that." This is how you do private fields within classes in Python, here is how you do protected ones.
And of course, doing neither of those, makes it just a normal type.
OK, so here is our PetSnake in a graphic.
We saw if we wanted the age and the name to be completely private, we use double underscores, if we want to have a protected variable that we want to strongly encourage people to stay away from, we use single underscores and you saw that we get warnings on the linters and things like that, so if we go and write some code that tries to access this type, here we can see we are creating a PetSnake called a py we'll get to this property thing in a moment, if we want to say "py._protected", we can, but that does give us a warning, if we try to say "py.__age", we saw that it crashes and basically that name doesn't exist, it's technically rewritten to be kind of hidden but normal access doesn't work for it.
|
|
|
show
|
4:45 |
One of the primary reasons people will write non-Pythonic code is they come from other languages that have other idioms and they just move their code over and make them work using the same former idioms and not really adopt the new Python ones.
So here we have some NotSoPythonicPet that we've been playing with, it's got some private fields - age and name, we'd like a way for us to get the name and get the age but not set it, here we wrote a get_name and get_age, so that you can get those.
But this is not Pythonic at all, and when you use the code, it's not pretty, it looks something like this, so here we create a NotSoPythonicPet, it's going to be a cow called Betsy who is 4 and we can say she is named such and such and is however many years old, so "cow.get_name", "cow.get_age".
It doesn't have to be this way, let's see how it should be.
All right, so here is the Betsy code again, not so Pythonic, we are doing this and this, let's go down to this PetSnake type that we are working with and do something different, do it better.
You should almost never write these getters and setters in Python, instead, the much more natural way to work with this would be to say "py.name", "py.age" as if they were a field, now this can be just accessing underlined variables, these could be computed like in a shopping cart you could say "cart.total" and maybe that just actually does a loop and adds up all of the items, but as a consumer, you don't want to think of these as functions, you want to think of them as just attributes of the class, right?
So in Python, instead of writing those getters and setters, we can say come over here and say I'd like to have a function called "name" and this is going to return "self.__name", now if I try to run this code, and let's do the same for age, and if I come down here and I write this code, we are going to get something entirely unexpected, what do you get if you say the name of a function?
Without parentheses, you get the bound method, bound to this object.
That's not what we wanted, so then we have to say this, and that's not so pretty, technically it works, but we are kind of back to the previous example that was names for our getters, so in Python we can use a decorator called a property decorator, from the built-ins, down here I can say actually this is not a regular method but a property and now if I say "py", well if I say it far enough down, "py.
name and age" you can see the little "p" by there, and if I access it like this, this actually just calls the function, beautiful, right, don't write getters, write this.
Suppose I want to be able to change the age but not the name, if we try to set the age, right now it's read-only, obviously, and it says can't set the attribute we've already got this read-only property called age but if we wanted to set the age, we can come down here and write another function called "age", that takes the value and we'll say "self.__age = value".
Now we give it another attribute up here, we say "age.setter", now this is less delightful than just add property but that's how it works.
So now we should be able to set the age and run it, first our snake is 6, then 7, so just to make it clear, these are actual function calls, not just changing the underline property, I'll do a print, there, so all right, two little prints that every time you execute this code, which could do anything we wanted to do, we just happen to be setting the underlined private field, it will print this and then when we get it will print that.
So here you can see, "Here is my pet snake", all we are getting is age, its name and age and such and such, setting the age, getting the age and so on.
And finally like I said, you can have computed properties, aren't really backed by underline store, so here I could say let's have "is_protected", we could do return True or False depending on how high the protection level is so we'll say, let's say "self.protected level value is greater than 5", so if it's greater than 5, the snake is protected.
if it's not then it's not, whatever that means.
so we'll just at the very end I'll print "py.is_protected" you can see this property read-only property, run that, no, the snake is not protected.
All right, so this is not based on just returning something, we can compute whatever we want to.
Properties are really useful, very Pythonic and I recommend that you make good use of them.
So let's see in a graphic how we evolve this, right, getter/setter - bad idea.
In our Pythonic pet, our PetSnake, we've got our age and name and here we are writing a property that says get me the read only version of the name and the read only version of the age.
We also saw we can make writers or setters for the properties, as well as computed properties that are not just returning underlined fields.
So with this in place, we can write as a consumer of the class, much more natural code.
If we create a pet, it's called "py" and its name is "py.name" and its age is "py.age".
|
|
|
|
8:50 |
|
|
show
|
2:27 |
Loops in Python are a little bit different than loops in other languages.
You'll see that there is much more collections philosophy underlying them.
Let's start with the basics.
There is no numerical loop in Python, there is no "for" loop, like C++, C#, Java, Javascript, they have this way of walking through a number and incrementing it usually to pull items out of an array, so I imagined what would that look like in Python if we had a numerical "for" loop, something like: "this for i = 0; i less than len(data); i++ " we are going to go work with items.
Well, that doesn't exist.
Sometimes, people try to work their way around it using the loops that do exist and recreating this more or less.
Look, we've done it, we've taken the initialization of the variable, moved before loop, we have the test and now withing the body loop we do the increment.
Perfect.
No, technically that works but this is also super non-Pythonic so let's look at some code that is.
All right, here in PyCharm you can see I kind of sketched out what that might look like, well as you saw we can well, first of all, this just put any ideas out of your head, this doesn't round right, obviously.
There is no "for" loop, but we can fake this idea we can say the "i = 0" goes here, this can be a "while" loop, we can do our test there and this increment bit, we can put that down here.
Like so, we don't have "++" but we do have a "+= 1", let's see if it works, it should put out 1 and 7 then 11, oh but of course, it does not, let's do this.
Now it prints out the index and it prints out the value.
All right, this is not Pythonic, so we'll just make a note: "No, NOT Pythonic".
So of course, what is the proper way to loop through these items?
"for item in the collection" and let's print this out, instead of worrying about the index, we just have the item let's put a new line in between, there: 1, 7, 11.
Perfect.
No fuss, no muss, just go.
So, there is no numerical "for" loop or faking it like this, also not Pythonic, we'll talk about what you can do when you really need that later, but typically, write loops like this.
OK, in a graphic, no numerical "for" loop, instead just loop over the data, usually the goal is to get at the underlying items and some sequence anyway.
|
|
|
show
|
1:50 |
So it turns out sometimes when you really do just want to work through a sequence from numbers, in order: 1, 2, 3, 4, or maybe even evens for some reason: 0, 2, 4, 6 and so on, so in Python we actually do have a way to do this, so over here imagine we wanted this code that went from 0 up to 10 but not including it, what do we do?
Remember, there is no "for" loop, so we just say "for i in" and we can create this generator that goes from 0 to 10, and we could even use the step size if we wanted to change the increment there, instead of "+= 1" we would do something else.
All right, so this should go from 0 to 9 in the print out.
And it does, so here we can use range, now range is considered slightly dangerous for large values here, in Python 2, because if we look at range, like so, it just says range 1 to 7, let's put a new line here, like so, it says just 1 to 7, this is technically a generator, but if we did this in Python 2 up here you can see this has just bin/Python, which is Python 2, what we'll get at the bottom is no longer a generator, it's a list, so if you put 10 million here instead of using the generator with the yield slowly create this, it actually generates a list of 10 million items.
All at once.
And then, lets you loop over it.
Not amazing, right?
but in Python 3 this is no problem, if you want to do this in Python 2, "xrange" is your friend, now you get basically the equivalent of Python 3 "range".
Great, so if you really want to step through numbers, just use range, that gives you something that's iterable and you use that in a "for...in" loop.
Yeah, so in some sense there is a way to do a numerical "for" loop, it's just not a language construct, it's an idiom.
|
|
|
show
|
1:47 |
So in some sense we saw that range gives us a kind of a numerical "for" loop and that lets us walk through numbers from some starting point to some ending point, evenly incrementing them, continuously by the same amount.
If you actually want to get items out of a collection, if you are going to emulate that original "for" loop where you say "I am going to get the index and then index into some kind of collection like a list or something", still, don't do that, don't do that with the range, there is yet a better way.
So sometimes you want the item and you need the index at which that item comes from, suppose you are making like an ordered list type thing, item number 1 is this, item number 2 is that and so on, that might look kind of like this fake "for" loop up here, right, so we create the index, we do the loop based on the index, we get the value and we print out the index and value.
We can use a really cool combination of tuple unpacking and a special type of iterable that we can work with, so simulate this in a much more Pythonic way, so if we wanted to write this code we could write something like "for", let me just suspend what goes here for a minute, "something in" we can say "enumerate" and when you enumerate some kind of collection like in this case we'll enumerate "data", so what actually comes out is a tuple of 2 items, first the index and then the value for that part, to the loop, so we can unpack that in two variables right here, index and value and then we can do whatever we are going to do, here we said something like this: "we'll print out the index and the value", there you have it, if we are going to make this sort of ordered list style, you might put a "+1" here, item 1 goes to 1, item 2 is 7, item 3 is 11.
There, that's the Pythonic way to do numerical "for" loops.
So we saw that range works for just walking through a set of numbers, but if you actually want to get the items and the numbers, or items and the indexes rather, use enumerate and unpack the tuple into the indexing value and it can't be easier.
|
|
|
show
|
2:46 |
One peculiar feature of Python loops is that they have an "else" block, first of all, do you know that the "while" loop and the "for...in" loop have "else" clauses that you can attach to them?
Second, can you remember the order in which these happen, what triggers the "else" block to run versus it not running?
Let's have a look, so here we have two "while" loops, one "while" loop runs to completion; the other "while" loop breaks out early, let's just run to see the output.
Cool, so here we have 5 dots and here we have 4 dots, that means we've run through one all the way to the end, the other we stopped a little bit early.
So, there is nothing special about that, but let's see about the "else" clause here, so let's say "for all loops" we can say "else", so "do the loop, else", we'll just put a message to know that it ran or didn't in the "else" clause, so we'll write something like this, "in the else clause of the whole loop", and down here we'll say "else", in the "else" clause of the early break loop, which one is going to run?
Let's find out.
OK, so if we run through the entire loop, and we go all the way to the end, this becomes False, and then "else", we run this.
On the other hand, if we go through here and we never go to a case where this is no longer True but we break out early instead, we don't run the "else" clause.
I am sure there is a few good uses for this, somewhere, it doesn't seem like a language feature that's worth it to me, but my recommendation for Pythonic code is: Do not use the "else" clause on loops.
Yeah, here is a whole language feature, I say don't use it, now you might say, "Michael, is that really Pythonic?
I mean it is a language feature, who would say "Don't use a language feature that was put in there by Guido Van Rossum, the creator of Python himself?"" let's see.
Back in 2009, somebody asked about the "for/while/else" without "break" or "return" clauses and Guido dropped in and the guy said, "Well, I am not sure that this is a great choice of words", and Guido dropped in and said, "You know what, I would not have this feature at all if I had to do it over".
"I would not put the "else" clause on loops in the language, period." That to me is a pretty strong statement that you know, we don't really need this, there are many successful languages that don't have an "else" clause, I think the "else" clause is confusing, Guido thinks it's probably not the best to put it in there, let's all agree to avoid it.
Right, so we saw that we have "else" clauses here, if you break out the loop early in this case, the "else" clause does not run, if we run the loop to completion, basically to a False state, then it will run.
"I would not have put the "else" clause in the language at all if I had to do it over", to me it sounds like non-Pythonic.
|
|
|
|
13:32 |
|
|
show
|
3:56 |
Tuples play a central role in Python, we are going to look at variety of techniques and ways to use tuples that are particularly Pythonic, let's start with assignment and unpacking, and we'll start in code.
So, you probably know that tuples are defined like this, so it could be a number, another number, a string, even be like an array.
So if we wanted to just look at the our little creation here, we can go like this, we'll see that it's actually not the parentheses that have anything to do with this, usually, we could just as well write like this, and we get the same output, it's the commas, not the parentheses that make the tuple.
In fact, we can come down here and can have a shorter one, like this, sometimes you want to have a tuple with just one element in it, we could write this, there is a tuple of length 1, let's find out.
There, a tuple of length 1.
So that tuples, they can't grow after they are created, they are basically immutable objects that it can be added to or moved, things like that.
So that's not the Pythonic thing, that's just tuples.
We get values out of them like this, if we wanted to say print out the word "cat" that's in the second index position, zero-based, so there we'd print "cat", if we didn't actually do this, there that prints "cat", so the first thing we want to look at is unpacking these into variables, let's go over here and work with the shorter version, so let's suppose we had the number 7 and the word "cat" and that was all, if I want to have 2 variables, one for the number and one for the...
let's say animal, I could say "n for number = this" and I could say "a for animal = that", that would not be Pythonic, instead, what you would say is "n, a = t", and Python will unpack the first value into the first thing here, the second value into the second thing there, and so on.
Now, if we had another one, like another number here, and we try to run this, you'll see it crashes because it says too many values, so if we are doing that we would typically say I don't care what this value is and use an underscore to say "please ignore it", so let's run that.
And PyCharm is just saying "look you assign these values and you never use them here", so let's do this.
Now, maybe we should show you what numbers came out or what values came out of there, so we'll say like so, "n is 7", "a is cat", beautiful.
And underscore, well we could grab it but we don't care, that's the whole point of it.
So this concept lets us assign values in a single line so I could say "x, y = 1, 2", then I could print "x" and "y" and I would get 1 and 2.
Finally, this tuple unpacking is a very important when we are talking about loops, remember our numerical "for...in" loop where it gives us both index and the item, we wrote something like this: "for index, item in enumerate", something like this, for enumerating over a collection, we'll get the index and the item, so 0 had 1, "cat" and so on, there, 0 goes to 1, 2 goes to "cat", well this returns a tuple and we unpack them into index and item, so this tuple unpacking is super important and we'll see more of it as we go through this chapter.
So we saw we can create a tuple, we can unpack it into a variety of values, should we have a tuple of 4 values, we unpack it into greeting and one into enclosing, then we just print them out, you see the values come out as if they had been pulled out individually, we also saw that enumerate returns tuples and the way that we actually separate the values in a really nice clean way maybe didn't even notice this one has happened is we are actually using tuple unpacking into those two items as it comes back from enumerate.
|
|
|
show
|
1:24 |
Let's see the Pythonic way to swap two values and hint: It involves tuples.
All right, so here we have two values, "x" and "y", you can see we'll print them out here and we'll print them out there and our attention is to do some sort of swap thing.
Let's just run it really quickly.
All right, obviously not swapped yet, let's swap them here.
In most languages, this is sort of a 3-step process, you'd say something like "temp = x", "x = y", "y = temp".
Now if we run this, you'll see they should be swapped, great, 7, 11, 11, 7, but this is non-Pythonic.
And let's even teach PyCharm: "Hey, that's a word".
OK, so if we are going to do this in a Pythonic way, we are going to use tuples, and it turns out you can do it in a beautiful concise one-liner by temporarily creating a tuple and then unpacking it into the same variables but in reverse, so we can say "y, x = x, y".
Remember, the comma here creates a tuple and then the stuff in the left hand side will unpack that tuple back into the values but it unpacks "x" into "y" and unpacks "y" into "x".
Beautiful, one line, very Pythonic, let's see if it works.
Ta da, same thing, much cleaner.
Want to swap two values in Python?
Create a tuple and unpack it back into the reversed set of variables, so here we have "x" and "y", we say "y, x = x, y".
Swapped, one line, very Pythonic.
|
|
|
show
|
3:28 |
Sometimes you need to return more than one value from a function.
Let's see what the story of that is in Python.
So over here we have a non-Pythonic way to return more than one value from a function, now in Python, we don't have the concept of reference parameters, passing a pointer by reference, we just have passing the pointer, which lets us work with the values.
Some languages you can do things like this, you can say "int & val 1, int & val 2", that would be like C++, and say C# you might say like this: "out" or "ref" or "in out", things like this, we could even, if this was pass by value, we could even pass a pointer and then let it change, there is lots of things that some languages let us do, Python doesn't let us do that.
So here is one way which we can kind of do this in a kind of a hokey way so here we are passing in some value to work with, we want to compute 2 values and return both the values, so here we are going to pass in a list, and if the list is empty we are going to make a spot for 2 entries, otherwise, if the list is not length 2, we are going to complain and say "Oh this is not really what we are looking for", we wanted either a list with 2 elements or an empty list so that we can stuff the two return values into them.
Do a quick little bit of math and back here we get the values out and we pull them out, this is super non-Pythonic.
This is bad, so the question is: "Can we do better?" First of all, let's see if we pass in 7 that we are going to get the right values.
49 and 18.52 Those are right values, but the code, not so right, so let's take this and have a good version.
Keep that one down here, we'll make this one to be Pythonic, we'll just call it out_params, and we are going to do something entirely different.
We are going to get rid of all the stuff, this link, all this junk, watch how much simpler this gets.
So we'll have, let's say, return value 1, those are not good names in general for variables but maybe just to make a case of look these are the two values we are returning, we'll call of this.
So we can come down here and we can return a tuple and we can say that just say "r1, r2", that defines a tuple, that's one thing, we'll return that.
That's a little bit like what we were doing before with our list, so we could like say "return a list" but the thing that's cool is the tuple unpacking lets us get at that value really easy, so we can come over here and we can say we would like to call this function out_params with the value 7, we'd like to capture the values, remember, it's coming back as a tuple, so we can unpack that into individual values and give basically the appearance that our method is returning more than one values, we can say "v1, v2 = this", I can print out let's say the good version instead of this funky stashing stuff in the list, we just say v1, v2.
Now it literally looks like this method returns more than one value, but the trick that facilitates it is of course tuples and tuple unpacking.
Perfect, besides a little bit of spacing, it looks identical.
There, identical, so much better.
So we saw we can fiddle with collection types to make it sort of possible to return more than one value, this is really a bad idea, don't do this kind of stuff, instead, leverage the ability to create and return as single tuple and then unpack them as if they were multiple values, so here we are calling compute values, return it to tuple, we are unpacking that into two variables we are calling "b2", and "b32", and we are printing them out.
Wonderful.
|
|
|
show
|
4:44 |
We've seen how central tuples are to many parts of Python, let's look at a better version of tuples.
So over here I have a very simple program; we have two methods, "main", which is going to print out some data and it's going to get that data from this get_data_tricky version, you probably wouldn't call your function tricky but you know, just to highlight it for the course, right?
So you can see it returns a list of tuples, here we have some incrementing numbers, so maybe this is an id, we have 3 values here in the middle, so those must represent something important, we'll see, not totally sure what that is.
So we'll come over here, here I've got a little template for printing out some stuff and notice I've got some values just so it can run, so here we've got 3 things back and I just put "ones" everywhere.
Suppose I want to print out the id, the rating and the position.
Now remember, this is not the function I am getting it from, so maybe you don't have it handy easy to look at, so we are going to come over here and say well, I think that I remember the first one being this and let's see the rating maybe that was next, and the last two got maybe those represent the position and we know that doesn't look right because these are like floating point and that's like and integer, so maybe actually this is a 3, what was that, that was 1, yeah, yeah, OK, so that's right, so this is what we wanted, 0, 3, 2, 1, what if I wanted to add an item, a thing, another element to this tuple?
How easy this is going to be to maintain, to review, to bring on new people, and so on, this is not a good way to work, so let's talk about a better kind of tuple.
so let's import collections, and let's define something called a Rating.
Now this is like defining a class or something like that, like a custom type, but we can do it in a very concise short way, using "collections.namedtuple"s.
So what you put here is the name, the type name, and then you can put the fields separated by commas, so maybe we want to call this id, rating, "x" and "y", something like that.
So now, give us some space, so PEP 8 is not mad about our spacing, we can write a better version here, instead of doing all this, let's have a rating, just like the way you initialize a class, or something like that, here we are going to initialize our rating and it takes an id and a rating and then "x" and then "y".
Actually, it looks like I have that wrong, so let's put it like this, or I would have to reorder my data but let's say it goes like this.
Now, let's comment out this tricky version, here we go, the data from the better and we'll hide this, it didn't even matter what order it comes in, we don't care, we don't have to look at it, so we are going to say now we are going to work with this better version of data, I want to put the id first, so let's see what is that, "d." all right, "id".
Cool, and we are going to have "d.rating" I think was next, "d.x", "d.y", see how much nicer that is?
And literally, that is all it takes, name the type, state the basically the names of the positions, and then when you allocate it, instead of just saying regular tuple like this, you just allocate it as an instance of a class.
So let's run it, make sure I didn't pull any sneaky tricks, that it still works, boom, id 1, 2, 3, rating looks right, position x y, great.
And, these named tuples, they have all the properties that you would expect, so for example, I can come down here I could say let's say we want the x y value so I could have, so here, like this, I could say I want to unpack this tuple and I want to print x and y so you should just see just the numbers next to each other alongside the other values.
There is the x y values we are unpacking.
So these are regular tuples, they do everything regular tuples do but they are upgraded and have names, wonderful.
So to create one, we just import the collections module, we create a collections.namedtuple, we give it a name, we catch the instance of the class, generate it from name tuple here, and when I use that every time when I allocate one of them.
We name the positions, this case we have temperature, latitude, longitude and quality, then you can see we create one and we can access it in the traditional style in bracket 0 but much better "m.temp", "m.quality".
We print it out, we even get a nicer looking string friendly version rather than just the basic tuple without the names or understanding of what the positions mean, so named tuples, very Pythonic, definitely make use of them.
|
|
|
|
11:13 |
|
|
show
|
3:14 |
Let's round out the course with a little bit of Python for Humans, and that's a bit of a play in words from some of the most popular open source projects that really add power to Python.
This section we are going to look at two separate external packages and how simple and lovely they make it to work with certain types of data and we are going to do this because it really is meant to be a stand-in for look at open source, look at PyPi and look to the community and ecosystem before you start working on your project for all the things that you can build your project from.
There is an amazing set of lego blocks out there all you have to do is know to reach for them.
So if you find yourself thinking "hm, how am I going to implement this bit?" of whatever subsystem you are working on in Python, stop and do a little research first.
For example, if you are going to work with user accounts, and you need to store user names and passwords, you hopefully know that you should hash those passwords.
Did you know you should use separate salt per user to go into hashing their password?
Did you know that you should fold that hashing over and over and over again to make it computationally difficult?
Not five times or ten times but something like a hundred thousand times.
So if you are thinking oh my gosh, this is going to be a lot of work, that's one way to think about it, the other one could be "oh, there is a really great library for exactly that thing called passlib", go grab that, OK?
So when we look at these two packages yes, it's great that you know about them, but the most important takeaway is not the details of the two packages we are going to focus on, but really the concept of there are so much out there to work from you really should start there.
Right, so the first place to look is probably PyPi, the Python package index and you can see at the time of this recording, there is 82 000+ packages there, so about 300 new unique packages a day, and the power of what's available here really is the main reason why Python is popular.
Another really important place to look for Python libraries and tools is of course GitHub.
So there is this really cool site called GitHut.info, let's check that out quickly.
So here you can see, these are all the popular languages on GitHub, and here is their active repositories, the total number of pushes, number of forks, how recent it was, what year it appeared and you can actually hover over these and it tells you all sorts of things, so for example we could compare say Python to C#, to Ruby and you can see that Python is more popular than Ruby, way more popular than C#, anyway, GitHub is such a central part of modern software development and look where Python lives, we have Python, we have Java, and we have Javascript.
Now, my interpretation of this data is that Javascript is not really earning its position here, I think this counts the Javascript that are in the Java websites, the Python websites, the PHP websites, the Ruby websites, the C# websites, and so on, so I think Javascript is being over counted here, so either way, Python is either 3 or 2 on this list, so certainly, look to GitHub, look to PyPi for your packages and your features before you just write the whole thing from scratch, remember, Python comes with batteries included, these two places are often where you find those batteries.
|
|
|
show
|
4:19 |
The first of the two packages that we are going to look at is the Requests package.
It turns out the Requests is the most popular package for Python, let's look at its website really quickly.
So over here you can see HTTP for Humans, very nice, "the only Non-GMO HTTP library for Python, safe for human consumption", basically the idea of Requests is the urllib, urllib2 that are in Python, are cumbersome and hard to work with and overly complicated.
Here is a re-imagine of it by a guy named Kenneth Reitz who does amazing work to make it much more delightful and easy to work with.
You'll see this package gets a little bit of traffic, so if I search for downloads, Requests is one of the most downloaded Python packages of all time pulling in over 7 million downloads every month.
Think about that, 7 million downloads a month.
And it's been around for really long time.
There is actually some talk about making Requests the new urllib more or less like bringing this into the standard library to keep Requests more agile, they decided to keep it out, nonetheless, Requests is even recommended over the built in URL libraries: urllib, urllib2 and so on.
So let's do something awesome with Requests, so over here we have a URL to the omdbapi, that's the Open Movie Database API, and we can do search here and get the data back as JSON and do a search for some text so we are going to ask the user to enter some kind of text like "enter the name of a movie" or whatever and it will go pull that down.
We did play with this in another example previously but we didn't focus on Requests.
So in order to do this, the first thing we have to do is get started.
We've already installed Requests, and of course, we talked about pip and packaging and pip installing various packages but also from PyCharm we can come over here and look at our current environment and see that we already have Requests installed but in fact it's a little bit out of date we won't mess with it, but we could upgrade it.
If we didn't have this installed we could hit "+" and say "hm, I am looking for Requests", it turns out there is a lot of stuff that's built upon Requests here, did you know there is requests-middleware, requests-guards, requests-ftp, requests-cloudkit?
All of these things, but here is the one that we want and we can just hit "boom, install" but great, it's already installed.
So let's just use it, remember "import antigravity"?
Well, here is "import requests".
So the way it works is we get a response back and we give it some URL here, and URL we are going to construct from the user text, we probably should check "if response.status_code" is not equal to 100, print, "wow, that is code such and such".
All right, so hopefully we don't end up in that case, but you never know.
Now let's go down here and actually get the data, so we made this request and everything was OK, we'll say that the data is going to be response.json, so that's going to actually finish downloading all the text and the response, convert it from json into a dictionary so this is going to be like a movie lookup.
Now, the format of this json is a little funky, if we actually want to search data, we have to go and ask for the search text here and then we can say "for m in search" and we could print out just the title of the movie we are looking for, and that comes in as title, something like that, and great, that's it.
Access is API, download it, possibly even authenticate against it, all we'd have to do is put the user name and password in here and we are done.
So this is just part of the power being leverage all these amazing packages on PyPi, let's see if it works, that would be a good thing.
So I want to search for let's say "Night Rider" can we find it?
I don't see Night Rider but there sure is a bunch of stuff about nights, let's try one more, see if Silicon Valley is there, Silicon Valley fantastic, the Spirit of Silicon Valley, the Hermits of Silicon Valley, all those things, and we didn't get just the title back, we got lots of data, like that, we just happened to only be printing out the title.
So here is one piece, one example of looking just beyond the standard library out in the broader ecosystem where you'll find amazingly powerful packages to help you, here it is in a graphic, we'll say "import request", generate the URL, "requests.get" given the URL, check the status code, otherwise, we'll just call .json, pull out the data boom, couldn't be easier.
|
|
|
show
|
3:40 |
Next, sticking with our some amazing package for humans, let's look at Records.
Records is also by Kenneth Reitz and I chose his work because I really admire him and I think it brings a great simplicity and powerfulness all together at the same time.
So here we have a thing called Records, it's an improvement on the built in DB API that lets you query databases in a really nice way, see it supports things like Postgres, MySql, SQL Server, Oracle and so on.
So let's go see how we use this to access to the simple little database.
Now here I have a little bit of starter code and we are going to go, let's just look at this little support file, it's going to go and find this demo_db.sqlite and it's going to generate a connection string to that file.
And if we look what's in here, let's go over here, you can see there is some ids, x y and values.
And so what I want to do is do a query based on this value, so I want to find all the measurements that have a value greater than 0.9, 0.95 and so on.
So how do we do that?
Well, I've already installed Records, here you can see Records and hey we have the latest version, cool, but again we could go install it from PyPi, with pip or with PyCharm, so we'll say "import records", and the way we get started is we create a database and we give it the connection string, like so, and then we say "db.query()" over here and we just give it some SQL.
Remember the tagline, "just write SQL", so we are going to come over here and we are going to do a query, now what I am going to write would normally just be a string, this is SQL embedded in Python, so there is no less support for whatever that means anyway, but because PyCharm over here has this database registered when I drag it across like that, watch what happens, this is, I'll never get tired of seeing this, so if I type "SELECT" it's going to start to think oh, maybe you are writing a database query, not yet, if I say "* FROM", now it has, OK, we have two of these databases active so "SELECT * FROM" and now notice how I got syntax highlighting inside the string and now as I hit space I actually get completion on the column, so we get id and value, x and y, I want to say "where the value is > than 0.9", so there is a query, that's pretty easy, now let's loop over it, so "for r in" and let's just print it out to see what the heck came back here, so if I run this, there, you can see we got our records back from the database, and notice there is a bunch and they are not quite ordered the way I'd like, so let's say "ORDER BY value DESC", how easy is that?
Connection string, create a database, create a query, done.
And notice, we can come out if we just want to print the value, these have access to all the values, if I want to get just say the top 3 highest measurements or let's say top 5, we can use slicing, right on the results, boom, there is the top 5, beautiful.
So again, here is how you use Records, one import statement, create the database, run the query, done.
3 lines of code including the import and connecting to the database.
Again, just another example of how important it is to look around at what's available when you are working with Python apps, there is so much out there, one of the biggest challenges is actually finding it, hopefully, you are inspired to look around by some of these examples.
All right so the final takeaway of this whole section is: "It is Pythonic to leverage PyPi and open source more than it is to implement the coolest clever algorithm on your own code, and keep it private."
|
|
|
|
7:55 |
|
|
show
|
0:24 |
Congratulations, you've made it to the end of the course.
You've completed over 50 examples contrasting non-Pythonic code with idiomatic Pythonic code.
I hope you've learned a ton, I hope you have a new appreciation for some of the idioms built into Python, why we use them, what their advantages are and how you can apply them to your apps.
The ones you've already built and the ones that you are going to build in the future.
|
|
|
show
|
6:06 |
So let's just take a few minutes and review what we have studied and what we've learned.
We started out looking at PEP 8 and many people when they first start looking at Pythonic code and thinking about these idioms and these concepts, they might feel that, well, PEP 8 is what is Pythonic code, it defines how we write Pythonic code.
Yes it does touch on some of the things you should do in Python, it does talk about how you should write your code and even some of the underlying patterns that you use, but there is so much more, as you now know.
We talked about many foundational concepts and in some senses it's just kind of a grouping of a really important core concepts that didn't fit into their own category.
So we talked about thruthiness, booleans, leveraging the truthiness of objects, testing for None, remember, use "is", not "== None", we talked about multiple tests against the single value, remember we saw that Pythonic way to do this is value "in" collection or set of options, using "random.choice" to find a random item out of a sequence; we talked about string formatting, we saw that when you write scripts that are meant to be run as programs and chained together Unix style, you should really add exit codes for the error conditions, and we also saw flat is better than nested, in practice.
We next turned our attention to dictionaries and you saw a dictionary is really a core part of the Python language.
You saw there were tremendous performance benefits for using dictionaries for random lookup by values other than the index compared to other collection types such as list.
We saw that using __slots__ in certain limited situations can dramatically improve Python's performance around memory.
Python 3.5 introduced a new way to merge dictionaries, we saw that dictionaries can be a stand-in for switch statements, and we saw that dictionaries are isomorphic to JSON.
Then we turned our attention to generators and collections, generators as in methods using the yied keyword as well as generator expressions using the parentheses instead of the square brackets like a list comprehension.
We talked about using "in" to test for whether an item is in a collection or not, we saw slicing is a core Pythonic concept and can even be applied to outside of basic sequences like lists and so on, to things like databases.
For methods we saw that "yield" and "yield return" let us write simple and highly efficient generator methods; and finally, we saw that if we have a generator, regardless of where it comes from, whether it's a generator method or a generator expression, we saw a cool trick for summing up or counting the number of items in a generator.
One of the core building blocks for Python of course is functions.
And we saw the functions are first class citizens we saw that lambda expressions let us write small concise functions to be passed around as arguments, we talked about how using return values as errors from functions, while sometimes OK is generally, as a rule of thumb, frowned upon, and we should use errors and exception handling rather than return types to indicate failure, we talked about different ways to add polymorphism or overloading to functions, we talked about default values, variable number of arguments, keyword arguments, mapping dictionaries to and from keyword arguments all those sorts of things, and finally we saw one of the Python gotchas of which there is not many, but using a mutable instance or a mutable type for a default value.
Next, we came to import antigravity, talked about how amazing packages are and what the idioms around using packages and your own modules are in Python.
So remember, try to avoid wildcard imports, "from package import *", not super-Pythonic.
If you are building a module that is meant to be reused but also sometimes run as a program, you saw the "main", the __main__ convention in action.
We also briefly touched on virtual environments, using requirements.txt to help the consumer of your application know what they need to install.
Moving from functional programming into object-oriented programming we saw that classes and object oriented programming in Python are very important, and a key cornerstone of the language, we saw the right and the wrong way to add fields to the classes, we talked about data encapsulation and data hiding with underscore field name being protected and double underscore field name actually getting mangled by the Python runtime so that it's effectively private, although you saw that it's not really super hidden, you can still get to it.
And we saw that properties, both read-only and read/write are very powerful ways to encapsulate and protect our data and let the class manage it more itself.
Loops in Python are interesting because they are fairly different than most other languages, we saw there is no numerical "for" loop, there is only a sequence based "for...in" loop, but there are things to add into there, sequences we can use that will give us variants that are basically numerical "for" loops.
So remember we can "for...in" over a range and that will give us numbers in sequence, if we have a sequence and we want to "for...in" over that and get the index, we enumerate over that and project or unpack that into the tuple "index, value" and then we work with that.
We also saw that loops have an "else" block but we should forget that fact.
Tuples are powerful lightweight containers often used in Python.
And, we saw that we can unpack those into variables, so let's do something like "x,y =" tuple of length 2, put the first item in "x" and the second item in "y" and so on, and we can use that for all sorts of cool tricks, we'll use that when we do a "for...in" loop over enumerate, we used that if we wanted simulate returning multiple values from a method, remember, technically that's not what happens, but that's how it appears in code, which is wonderful; we finally saw that while tuples are great, working with them can be error-prone and kind of unclear, so upgrading them to named tuples via "collection.namedtuple" is a really nice way to work with them.
Finally, we took a look around the ecosystem for Python and said "there are so many amazing packages outside of Python", let's just round out the course by making a point that you should first look to things like PyPi, the Python package index and GitHub for the various building blocks or lego pieces of your application rather than trying to write them all from scratch.
|
|
|
show
|
0:32 |
So I hope that you've saved the source code from this class, you can see at "github.com/mikeckenendy/write-Pythonic-code-demos", we have all the code you saw me write during all the videos, so please take this moment, go over there and star that repository, maybe fork it, maybe download it, or at least bookmark it in your browser so that you can come back to it, it should be here forever but you never know, right.
Also, I want to encourage you to play with these ideas, and if having the source code to start from helps you play with those ideas in your own code, in your own project, then please do so.
|
|
|
show
|
0:53 |
If this dive into "what is Pythonic code", what are the idioms and the best ways of working in Python is interesting to you, I encourage you to check on my podcast "Talk Python To Me"; on "Talk Python To Me", I interview many of the great developers in the Python community, and our conversations often get around to things that touch on or hint at Pythonic ideas.
We've talked about SQLAlchemy, and I've had Mike Bayer on the show who is the creator and maintainer of SQLALchemy, we talked about Python For Humans, all done by Kenneth Reitz, he was on the show talking about Requests and APIs and so on, and that just gives you a sense of how you can dig much deeper in these topics, so if this resonates with you, go check out the podcast.
And before you leave, I want to take the chance to say "thank you, thank you for having the faith in me to buy my class, thank you for taking the time and spend it with me to make it all the way to the end." I hope you fond it really valuable and I'd love to connect with you online or offline, thanks again.
|